Data scientist interviews at Google are tough to crack. The interview process is rigorous, with challenging, company-specific questions across four or more rounds.
What kinds of questions can you expect? For starters, you’ll be tested on your knowledge of fundamental statistics and your experience designing metrics, A/B tests, and experiments.
You’ll face rounds testing your technical skills, but most importantly, you’ll face business case questions to assess your product sense.
The good news? With the right preparation, you can significantly improve your chances of landing that data scientist role at Google.
That’s why we created this comprehensive guide. To prepare it, we spoke with a Google data scientist coach and reviewed real candidate experiences from Glassdoor.
Below, you’ll find a detailed breakdown of the interview process, some sample questions, and expert tips—everything you need to walk into each round with confidence.
Here's an overview of what we'll cover:
- Role and salary
- Interview process and timeline
- Example interview questions
- Interview tips
- Preparation plan
Click here to practice 1-on-1 with a data science ex-interviewer
1. Google data scientist role and salary↑
Before we cover your Google data scientist interviews, let’s first look at the role itself.
1.1 What does a Google data scientist do?
Data scientists at Google (formerly known as quantitative analysts) are responsible for processing, analyzing, and interpreting data sets and using them to evaluate and make recommendations to improve Google’s various products. They’re vital to the company’s optimization and decision-making process.
There are generally two types of data scientists at Google: research and product. Though both draw on core data science fundamentals, their overall focus differs.
As a research data scientist, you’ll focus more on theoretical work (which could then influence product development). While your research could be applied to Google products, one of your main goals is to contribute to the field at large. This means publishing regularly in academic journals and collaborating with academic institutions.
On the other hand, if you’re a product data scientist, you’ll work closely with an engineering and product management team, making recommendations to ensure their decisions are data-driven. You’ll also be responsible for producing insights and metrics, communicating them to various technical and business stakeholders across the organization.
What tasks could you expect in your day-to-day as a Google data scientist? According to Enming (Google staff SWE and data science coach), you would generally work on metric design, A/B test, data analysis for opportunity sizing and impact measurement.
He also shares that on some teams, a data scientist acts like an ML engineer. “They focus a lot on data collection and modeling but their focus is mainly on model prototype rather than model deployment.”
Because Google is a data-driven company, data scientists apply their data expertise to work on various product lines, business functions, and research units.
These include Google Search, Ads Insights and Measurement, Google One, Google Play, Google’s compute infrastructure, Customer Engineering support, Google’s applied machine learning, Cloud Supply Chain Operations (CSCO), AI Safety Protection Team, Google Technical Services, and many more.
1.2 How much does a Google data scientist make?
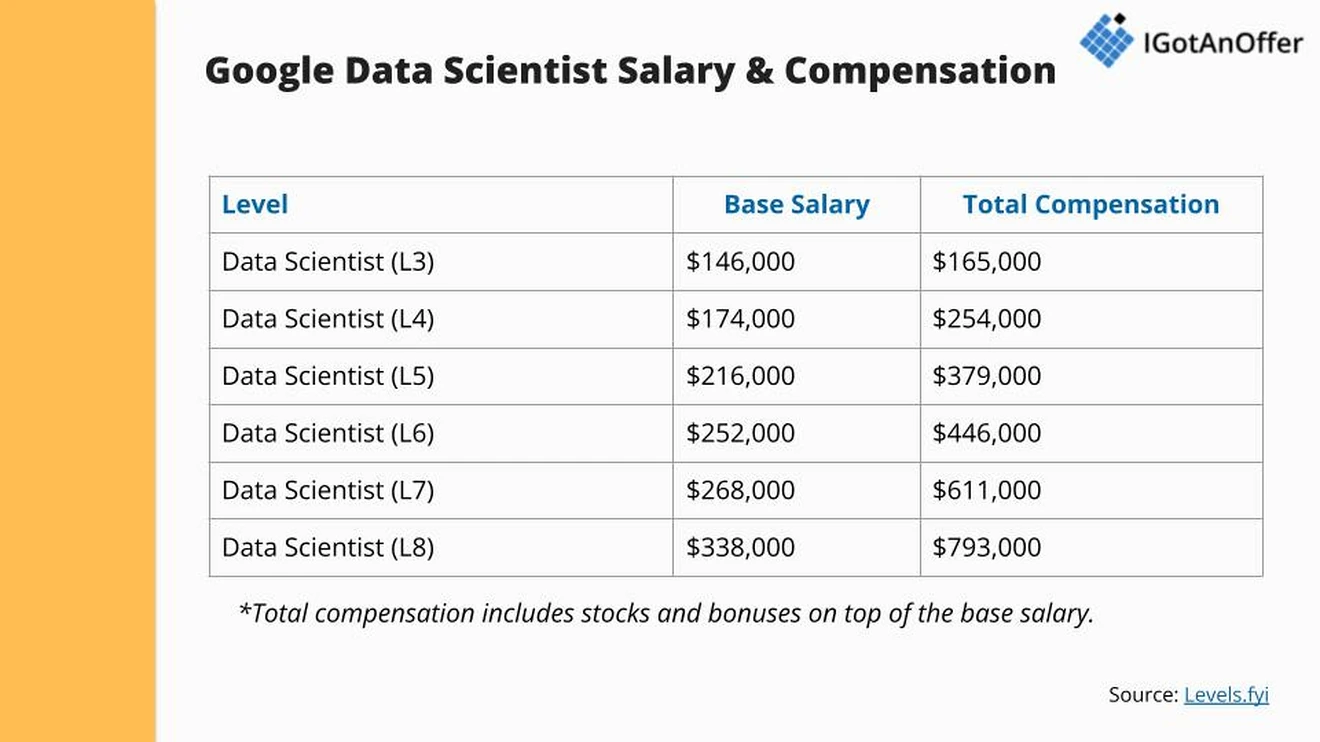
Based on Glassdoor data computations, the average base pay for a data scientist role at Google US is 45% higher than the estimated average base pay of a data scientist in the US.
Below you can see the average salary and compensation of the different data scientist levels at Google US, as of May 2025, based on Levels.fyi.
Ultimately, how you do in your interviews will help determine what you’ll be offered. That’s why hiring one of our ex-Google interview coaches can provide such a significant return on investment.
And remember, compensation packages are always negotiable, even at Google. So, if you do get an offer, don’t be afraid to ask for more.
Read our guide for tips on how to negotiate your offer at Google. If you need help negotiating, consider booking one of our salary negotiation coaches to get expert advice.
2. Google data scientist interview process and timeline↑
2.1 What steps to expect
What's the interview process and timeline at Google for the data scientist role?
It typically takes three to six weeks and follows the steps below. If you're interviewing at Google Cloud Platform, you can expect similar steps.
- Resume screen
- Recruiter screen (~30 min)
- Technical screen (~45-60 min)
- Onsite interviews (up to 5 interviews, 45 min each)
Note that the exact process varies slightly between positions, as Google data scientists may be working in either research or product domains. Your recruiter will send you information at the beginning of the process, which will detail what interviews you can expect.
Google has a dedicated Candidate Accommodations team that will help you through your application process if you require any special assistance at any point in the process. Be sure to fill out the accommodation form so that you can get the assistance you need.
Let's look at each of these steps in more detail below:
2.1.1 Resume screen
First, recruiters will look at your resume and assess if your experience matches the open position. This is the most competitive step in the process, as millions of candidates do not make it past this stage.
Check out our free Google resume guide with examples and our data science resume guide for help on writing yours.
If you’re looking for expert feedback on your resume, you can get input from our team of ex-Google recruiters, who will cover what achievements to focus on (or ignore), how to fine-tune your bullet points, and more.
After applying, you will receive an email containing a pre-screen questionnaire of introductory technical questions before moving on to the full technical screen.
This preliminary questionnaire will not be difficult if you are prepared for the full technical screen.
Note that if you got an internal referral or were contacted directly by a recruiter via LinkedIn, you may be able to skip the pre-screen online assessment.
2.1.2 Recruiter phone screen
After this, many but not all applicants talk to an HR recruiter on the phone. Come ready to answer questions about your professional background and why you’re interested in Google.
This call is also an opportunity to learn more about the interview process ahead of you as well as how to prepare. Your recruiter will walk you through what you can expect if you pass the screening. If you have any more questions, this is the time to ask.
The recruiter phone screen is typically followed by a technical screen. That’s why candidates are rarely asked coding or statistical questions at this step.
Some candidates report going directly to the technical screen after the initial application. In this case, the technical screen will include a few background questions that would otherwise have been asked in the recruiter call.
Be sure to specify with your recruiter ahead of time what type of screening you’ll have so that you can come prepared.
2.1.3 Technical screen
After the recruiter screen, you may move on to a video call with a hiring manager or one of Google’s data scientists.
This will take place over Google Meet. In very rare cases, you may undergo two technical screens before the onsite round. If you’re not sure what to expect, check in with your recruiter.
We’ll go into greater detail on the questions themselves later in this article, but in general, be prepared for a few background questions, followed by statistical questions and coding.
You’ll be coding live in a language of your choice on a shared document. Clear communication is important to Google, so practice talking through your reasoning simply and coherently as you work.
2.1.4 Onsite interviews
The final and toughest stage of the Google data scientist interview process is the onsite portion.
Typically, this involves five rounds of interviews. Each round lasts about 45 minutes, with time for lunch in the Google cafeteria if the interview is in a Google office. Other than lunch, you may have little to no breaks between interviews.
You will need to be prepared for many types of questions during the onsite interviews. Prepare for a higher level of difficulty than the questions presented during the technical screen.
More specifically, there are four main types of questions you’ll have to answer. We’ll give you practice examples later, but here’s a summary:
- Statistics and machine learning questions: where you’ll be tested both on general statistical principles and definitions as well as probability and applied machine learning.
- Coding questions: where you’ll demonstrate both technical skills and statistical problem-solving.
- Behavioral questions: where Google will assess your culture fit through your past experiences and current motivations.
- Product sense questions: where you’ll need to apply your statistical and coding skills to test and drive business and product decisions.
After you’ve completed the onsite rounds of interviews, you should receive feedback in a matter of weeks.
2.2 What the Google interview evaluation form looks like
At the end of each session, your interviewer will grade your performance using a standardized feedback form that summarizes the attributes Google looks for in a candidate.
This form is constantly evolving, but we have listed the main components we know of at the time of writing this article below.
A) Questions asked
In the first section of the form, the interviewer fills in the questions they asked you. These questions are then shared with your future interviewers. This is to ensure a well-rounded interview and that they’re not asking the same questions twice.
B) Attribute scoring
In the next section, each interviewer will assess you on the four main attributes Google looks for when hiring:
- General cognitive ability (GCA). Here your interviewer will try to understand how you solve hard problems, and how you learn and adapt to ambiguous situations. For more information, take a look at our guide to the Google GCA interview.
- Role-related knowledge and experience (RRK/RRKE). The company wants to make sure that you have the right experience, domain expertise and competencies for the position you're applying for. For more information, take a look at our guide to the Google RRK interview.
- Leadership. Google is looking for candidates with “emergent leadership,” i.e., a data scientist who’ll step up and lead at different times in the lifecycle of a project when their skills are needed.
- Googleyness (i.e. culture fit). The company wants to make sure Google is the right environment for you. Your interviewer will check whether you naturally exhibit the company's values, including comfort with ambiguity, a bias to action, and a collaborative nature. For more information, take a look at our guide to Googleyness and leadership interviews.
Depending on the exact job you're applying for, these attributes might be broken down further, but the total number of attributes does not usually exceed six or seven.
In this middle section, Google's interviewers typically repeat the questions they asked you, document your answers in detail, and give you a score for each attribute (e.g. "Poor", "Mixed", "Good", "Excellent").
C) Final recommendation
Finally, interviewers will write a summary of your performance and provide an overall recommendation on whether they think Google should be hiring you or not (e.g. "Strong no hire", "No hire", "Leaning no hire", "Leaning hire", "Hire", "Strong hire").
2.3 What happens behind the scenes
If things go well at your onsite interviews, here is what the process will look like:
- Interviewers submit feedback
- Hiring committee recommendation
- Team matching
- Senior leader and Compensation committee review
- Final executive review (only for senior roles)
- You get an offer
After your onsite interview, your interviewers will all submit their feedback usually within two to three days. This feedback will then be reviewed by a hiring committee, along with your resume, internal referrals, and any past work you have submitted.
At this stage, the hiring committee will make a recommendation on whether Google should hire you or not.
If the hiring committee rules in your favor, you'll usually start your team matching process. In other words, you'll talk to hiring managers, and one or several of them will need to be willing to add you to their team for you to get an offer from the company.
In parallel, the hiring committee recommendation will be reviewed and validated by a senior manager and a compensation committee. They will then decide how much money you are offered.
Finally, if you are interviewing for a senior role, a senior Google executive will review a summary of your candidacy and compensation before the offer is sent to you.
As you've probably gathered by now, Google goes to great lengths to avoid hiring the wrong candidates.
This hiring process with multiple levels of validations helps them scale their teams while maintaining a high caliber of employees. It also means that the typical process can spread over many weeks and sometimes months.
3. Google data scientist example interview questions↑
Let’s get into the four primary categories of questions you’ll answer during the Google data science interview:

Note that many of these questions are asked in the form of case studies. Take a look at our data science case study interview guide for more information.
In the sections below, we've put together a high-level overview of each type of question. In addition, we've compiled a selection of real Google data scientist interview questions, according to data from Glassdoor.
Note that the exact types of questions you’ll get may vary depending on whether you’re applying for a research or product role.
We've edited the language in some places to improve the clarity or grammar, and we've included a link to a solution when viable.
3.1 Statistics and machine learning questions
Google’s data scientists have to derive useful insights from large and potentially complex datasets. Thus, it’s imperative to have a strong understanding of statistics.
Out of all the question categories, general statistics and statistical probability come up the most often in all stages of the interview process. Take extra time to study this section.
In particular, you’ll want to focus on the basics of statistical inference. Practice explaining the core concepts in the most concise way possible.
Some general topics that typically come up include p-values, MLE, confidence intervals, and Bayes' Theorem. In addition to these general topics, you’ll find complete questions to work through below.
Your interviewer will also ask questions specific to machine learning, as Google data scientists must build algorithms that improve and remain accurate over time.
General topics that have come up before include regression models, feature selection, and recurrent neural networks.
Let's get to the example questions.
Google data scientist interview questions - Statistics and machine learning
General Statistics
- In what situation would you consider mean over median?
- For sample size n, the margin of error is 3. How many more samples do we need to make the margin of error 0.3?
- What is the assumption of error in linear regression? (Solution)
- Given data from two product campaigns, how could you do an A/B test if we see a 3% increase for one product?
- Is it good or bad if you apply bootstrapping on samples to increase your sample size?
- Predict some metrics using regression.
- If individual mean of two groups is rising, is it possible that pooled mean will decrease? if yes, then how?
- How would you design an A/B test for building a new YouTube feature?
- I have a deck and take one card at random. What is the probability you guess it right?
- Explain a probability distribution that is not normal and how to apply that.
- Given uniform distributions X and Y and the mean 0 and standard deviation 1 for both, what’s the probability of 2X > Y? (Solution)
- There are four people in an elevator and four floors in a building. What’s the probability that each person gets off on a different floor?
- Make an unfair coin fair. (Solution)
- Given a dataset, how would you determine which features are the most important for predicting a certain outcome?
- Describe an end-to-end machine learning project you worked on.
- If the labels are known in a clustering project, how would you evaluate the performance of the model?
- Why use feature selection? (Solution)
- If two predictors are highly correlated, what is the effect on the coefficients in the logistic regression? What are the confidence intervals of the coefficients?
- What is the difference between K-mean and EM?
- When using a Gaussian mixture model, how do you know it is applicable?
- Derive the maximum likelihood estimator for logistic regression.
- What happens to regression coefficients if you have omitted variable bias?
- Explain the difference between supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Give examples of each.
- Describe to me how PCA works.
- How would you evaluate the performance of a machine learning algorithm?
- Explain what Transformer architecture is.
- Can you describe how you would approach building a predictive model for user engagement on a new feature within our platform? Please walk through the steps, from data collection to model evaluation.
- What is the difference between boosting and bagging?
- Explain the workings of a neural network. Why do you think a sigmoid function is more beneficial as an initialised function or otherwise?
3.2 Coding questions
Google data scientists work with the company's vast datasets to understand and solve real-world problems. So expect Google interviewers to test you on SQL testing and basic Python codings, Enming says.
However, unlike Meta and TikTok data scientist interviews, which focus largely on SQL, you’ll see more statistical coding questions at Google. So be ready to write functions that solve problems related to statistical analysis and probability.
Most candidates report coding with Python, but you may use R or your preferred programming language. Just let your recruiter know beforehand.
SQL questions are the second most frequent technical topic. Google is looking for candidates who know how to use and manipulate important data. So practice running SQL queries quickly and with proper syntax, particularly for DS-product candidates.
Some candidates also report getting a mixture of questions on data structures and modeling, so you might want to brush up on these as well.
Google data scientist interview questions - Coding
Statistical coding questions
- Write a function to generate N sample from a normal distribution and plot the histogram. (Solution)
- Write code to generate iid draws from distribution X when we only have access to a random number generator.
- Coding in R, multiply all a[i,j] in a i rows j columns dataset.
- Given a list of characters, a list of prior probabilities for each character, and a matrix of probabilities for each character combination, return the optimal sequence for the highest probability.
- Given a list of numbers, calculate the sum of the odd numbers in the sequence of 100 numbers (I.e. sum(1st, 3rd, 5th … Nth number for in sequence ).
- Confidence interval calculation in Python (Solution)
- How are 2 time series different from one another?
- How would you find the top 5 highest-selling items from a list of order histories?
- Can you explain how SQL works?
- Given three columns of data, how would you compare the first three to the last three?
- How do you calculate the median for a given column of numbers in a data set?
- How would you optimize a database query?
- What are some ways to effectively reduce the dimensionality of a dataset? (Solution)
- How do you invert a binary tree? (Solution)
- How do you code the simulation model to get the probabilities of a given scenario?
- How would you approach a data analysis project where the data is very messy and unstructured?
Click here to learn more about Google coding interviews.
3.3 Behavioral questions
In addition to the question types highlighted above, you can expect to be asked behavioral or "resume" questions about your past work experience and your motivation for applying to Google.
Your interviewers are looking for you to demonstrate “Googleyness” as well as your ability to communicate clearly.
If you're applying directly to a job posting, be strategic by aligning your answers for behavioral questions with the top qualifications that are listed in the job description.
Below you’ll find real behavioral interview questions reported by data scientist candidates.
Google data scientist interview questions - Behavioral
- Why Google?
- How do you sort your priorities when engaged in multitasking?
- Describe a past project you worked on.
- In what direction do you see your career moving?
- Do you prefer working in small or large teams?
- How do you push back when disagreeing with a manager?
- What are the top competencies that you are bringing to our company?
- Why do you prefer Google over Apple?
- How is this job aligned with your objectives?
For tips on how to answer behavioral questions, read our guides on Googleyness and leadership interviews and Google's behavioral interview questions.
3.4 Product sense questions
According to Enming, aside from demonstrating technical skills and core statistics knowledge, you’ll need to showcase product sense as a Google DS.
After all, if you get the job, you’ll need to use your technical skills and techniques to test and improve Google's products as well as the company as a whole, and ultimately drive business decisions.
So come prepared to apply your technical knowledge to business or product case scenarios.
For example, Google tends to ask questions that use statistical A/B testing to compare the performance of their products and services.
You should also be prepared for questions about product metrics and how they could be improved.
If you’re applying for a DS-product role, don’t forget to familiarize yourself with Google’s main products in advance. If you’re aiming for a research role, brush up on Google’s latest publications relevant to the unit you’re applying to.
Practice using the example questions below.
Google data scientist interview questions - Product sense
- You have a Google app and you make a change. How do you test if a metric has increased or not? (Solution)
- How do you detect viruses or inappropriate content on YouTube?
- How would you compare if upgrading the android system produces more searches?
- The outcome of an experiment is that 5% of one group clicks more. Is that a good result?
- How would you measure the time spent in Google Search per day per user? If the average searches per day per user data goes down, but the average searches per country goes up, how would you explain it?
- How would you remove bias and make inferences from data about two ad campaigns?
- Given there are no metrics being tracked for Google Docs, a product manager comes to you and asks, what are the top five metrics you would implement?
- If product A had a feature and the team wanted to change it, how would you use data science to give recommendations to the team?
- How would you study the relationship between hours of YouTube watched vs age? What about confounds? Zip code, etc.
Click here to learn more about product sense interviews. This guide is written for PM candidates, but still contains insights you’ll find useful for your data scientist prep.
You’ll find that most of your interview questions will come in the form of product case studies. Familiarize yourself with the format by reading our guide to data science case interviews.
4. Google data scientist interviewing tips↑
You might be a fantastic data scientist, but unfortunately, that won’t necessarily be enough to ace your interviews at Google. Interviewing is a skill in itself, that you need to learn.
Let’s look at some key tips to make sure you approach your interviews in the right way.
4.1 Ask clarifying questions
To test your comfort with ambiguity, your interviewers will ask intentionally ambiguous questions. So be sure to ask clarifying questions and understand the problem before diving in.
Going straight to problem-solving without asking questions is a red flag.
4.2 Be conversational
Google wants to know if you have excellent communication skills. So make sure you approach the interview like a conversation.
The best way to approach an interview, especially case studies, is to treat it like you’re discussing the problem with a colleague.
Additionally, Google will be testing your ability to communicate highly technical concepts to non-technical people. Be sure to brush up on your basics and practice interpreting them in a way that’s clear and easy for everyone to understand.
4.3 Think out loud
You need to walk your interviewer through your thought process before you actually start coding.
Google recommends that you talk even while coding as they want to know how you think. Your interviewer may also give you hints about whether you’re on the right track or not, so listen carefully and be prepared to pivot if needed.
4.4 State and check assumptions
You need to explicitly state assumptions, explain why you’re making them, and check with your interviewer to see if those assumptions are reasonable.
4.5 Present multiple possible solutions
Present multiple possible solutions if you can. Google wants to know your reasoning for choosing a certain solution.
Google also wants to see how well you collaborate. So when solving problems, don’t hesitate to ask further questions and discuss your solutions with your interviewers.
Also, if you have a moonshot idea, go for it. Google likes candidates who think freely and dream big. So if the question allows it, try to find a way to display your creative and innovative thinking.
4.6 Be honest and authentic
Be genuine in your responses. Google interviewers appreciate authenticity and honesty.
If you faced challenges or setbacks, discuss how you improved and learned from them. If you’re asked about your failures, don’t disguise them as strengths.
Google values intellectual humility; admit where you went wrong and what you were able to learn from the failure.
4.7 Center on Googleyness
Familiarize yourself with Google’s core values and align your behavioral responses with them.
Google values certain attributes such as comfort with ambiguity, collaborative nature, bias for action, and focus on the user.
4.8 Brute force, then iterate
When coding, don’t necessarily go for the perfect solution straight away. Google recommends that you first try and find a solution that works, then iterate to refine your answer.
4.9 Keep your code organized
Google wants to see that your code has captured the right logical structure.
Make sure to keep your code organized so your interviewer won’t have a hard time understanding what you’ve written.
5. Preparation plan↑
Now that you know what questions to expect, let's focus on how to prepare. After all, the right preparation will make the difference between failing your Google interviews and getting an offer.
Below is our four-step prep plan for Google or GCP. If you're preparing for more companies than just Google, then check our generic data science interview preparation guide.
5.1 Learn about Google's culture and products
Most candidates fail to do this. But before investing tens of hours preparing for an interview at Google, you should take some time to make sure it's actually the right company for you.
Google is prestigious and it's therefore tempting to assume that you should apply, without considering things more carefully.
However, it's important to remember that prestige alone won't make you happy in your day-to-day work. What will make you happy is what you’ll actually be doing as well as the people you'll be working with.
If you know data scientists who work at Google or used to work there, talk to them to understand what the culture is like.
In addition, we would recommend reading the following resources:
- Google's mission statement (by Google)
- Google's values (by Google)
- Google strategy teardown (by CBS Insights)
- Google (Alphabet): Generic Competitive Strategy & Growth Strategies (by Panmore Institute)
- The Unofficial Google Data Science Blog
- Google Research
5.2 Practice by yourself
As mentioned above, you'll encounter four main types of interview questions at Google: statistics and machine learning, coding, product sense, and behavioral.
Below we’ve gathered free resources you can use to kickstart your prep per topic:
Statistics and machine learning
- Google’s technical development guides on machine learning
- Brilliant.org’s online courses on statistical probability
- StackExchange for questions and answers around statistics, machine learning, data analysis, etc.
- Reddit’s statistics and machine learning threads to discuss questions with peers
Coding
- Google coding interview
- Google’s technical development guides for more coding questions
- Practice for 3 types of SQL interviews
- SQL Course
- Mode Analytics SQL Tutorials
- Programmer Interview SQL Practice Database
- Python | SQL Comparison
- Data Transformations in R
Check out this coding mock interview by Google to get a sense of how Google conducts its tech interviews.
Product sense
- Product sense interviews
- Product metric interviews
- Favorite product interview question
- Product improvement interviews
- Estimation interviews
Note that these guides are written for PM candidates. But you can use them to practice a method for answering the majority of the product/business sense questions you're likely to encounter as a data scientist candidate.
Behavioral
A great way to practice all of these different types of questions is to interview yourself out loud. This may sound strange, but it will significantly improve the way you communicate your answers during an interview.
Play the role of both the candidate and the interviewer, asking questions and answering them, just like two people would in an interview. Trust us, it works.
Practicing for a data science role at another company? Check out our other company-specific guides:
- Meta data scientist interview guide
- Amazon data scientist interview guide
- Amazon applied scientist interview guide
- TikTok data scientist interview guide
- Uber data scientist interview guide
Once you’re in command of the subject matter, you’ll want to practice answering questions. But by yourself, you can’t simulate thinking on your feet or the pressure of performing in front of a stranger. Plus, there are no unexpected follow-up questions and no feedback.
That’s why many candidates try to practice with friends or peers.
5.3 Practice with peers
Practicing by yourself will only take you so far. One of the main challenges of data scientist interviews at Google is communicating technical concepts in a way that's easy to understand.
As a result, we strongly recommend practicing with a peer interviewing you. If possible, a great place to start is to practice with friends. This can be especially helpful if your friend has experience with data scientist interviews or is at least familiar with the process.
However, be warned, as you may come up against the following problems:
- It’s hard to know if the feedback you get is accurate.
- They’re unlikely to have insider knowledge of interviews at your target company.
- On peer platforms, people often waste your time by not showing up.
For these reasons, many candidates skip peer mock interviews and go straight to mock interviews with an expert.
5.4 Practice with ex-interviewers
Finally, you should also try to practice data science mock interviews with expert ex-interviewers, as they’ll be able to give you much more accurate feedback than friends and peers.
In our experience, practicing real interviews with experts who can give you company-specific feedback makes a huge difference.
Find a Google data scientist interview coach so you can:
- Test yourself under real interview conditions
- Get accurate feedback from a real expert
- Build your confidence
- Get company-specific insights
- Learn how to tell the right stories, better
- Save time by focusing your preparation
Landing a job at a big tech company often results in a $50,000 per year or more increase in total compensation. In our experience, three or four coaching sessions worth ~$500 make a significant difference in your ability to land the job. That’s an ROI of 100x!