Google’s interview process is long and arduous, seeming like a black box to many candidates. Not knowing what’s ahead makes it even harder to prepare.
We’re here to help. We work with 100+ ex-Google interviewers on our platform, who have helped thousands of candidates navigate the Google interview process and prepare effectively.
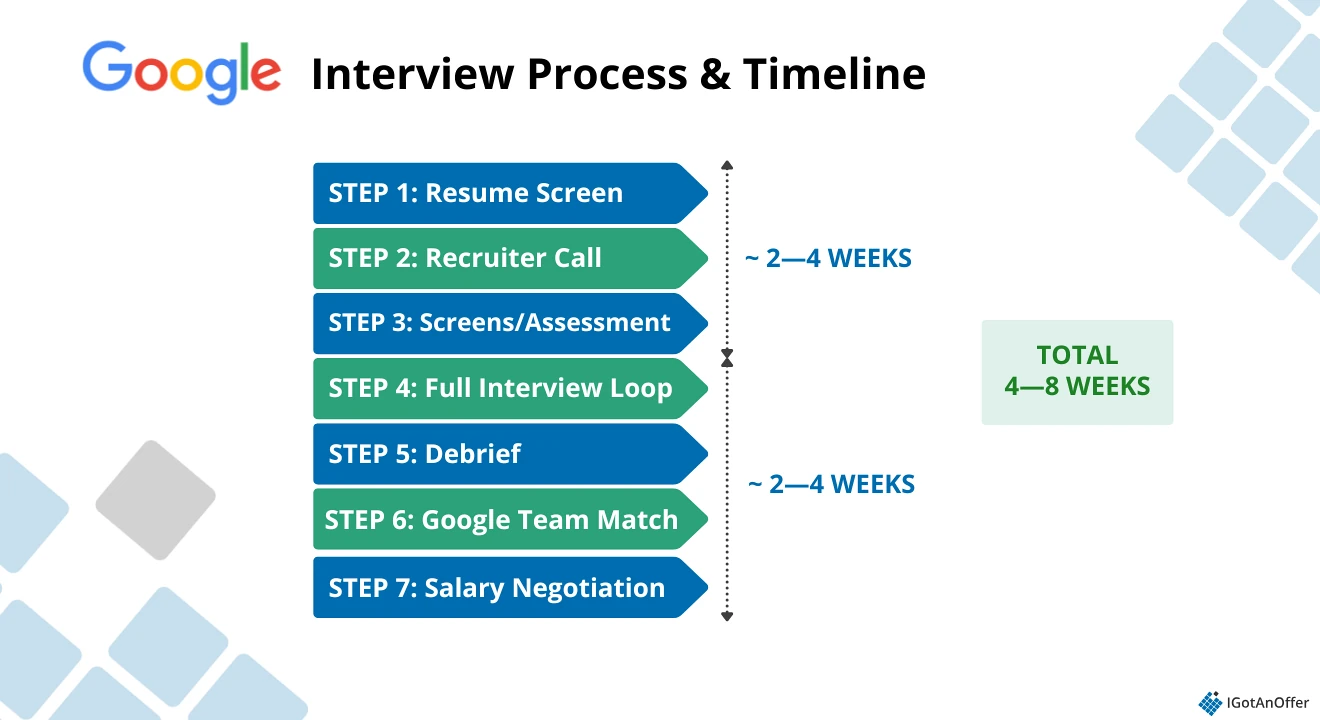
Here’s what you need to know: Google’s interview process takes around one to two months, and there are seven steps: resume screen, recruiter call, phone screen(s), onsite interviews, hiring committee, team matching, and salary negotiation. The steps that will require the most preparation are the phone screens and onsite interviews.
In the rest of this article, we’ll dive deep into each step of the recruitment process and how you can prepare for it.
Let’s get started.
- Step 1: Resume screen
- Step 2: Recruiter call
- Step 3: Phone screen(s)
- Step 4: Onsite interviews
- Step 5: Hiring committee
- Step 6: Team match
- Step 7: Salary negotiation
Click here to practice 1-on-1 with ex-Google interviewers
But before we get into each step, let's get to know Google first.
About Google
Google was founded in 1998 as a search engine company. It has since grown into a multinational tech company with several products and services, including Gmail, Google Maps, Google Adwords, Google Chrome, YouTube, and more. In 2015, as part of a corporate restructuring, Google became a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., a conglomerate holding company.
Alphabet (including Google) is currently valued at $3.39 trillion as a public company. It employs around 190,00 people in nearly 60 countries around the world. At the end of Q3 2025, its top products in terms of growth are Google Cloud, Gemini AI, and YouTube.
Working at Google
Inclusive workplace culture
Googleyness is a much looser workplace culture, compared to others like Amazon’s Leadership Principles. Instead of ‘culture fit’, the company looks for ‘culture add’, i.e., “Will this candidate bring attitudes and character traits that will be a positive addition to Google’s working culture?”
Hybrid work setup
In the last two years, tech companies have started mandating a return to the office, and Google is no different. It now requires remote workers to go to the office three days a week, and has even offered some a one-time paid relocation expense to move within 50 miles of an office.
Work-life balance
Based on Glassdoor surveys, Google’s work-life balance is rated 4.4. According to John Miller, a software engineer who’s worked at both Google and Amazon, Google gives better benefits and therefore encourages better work-life balance: “more vacation, more standard holidays, more leave for personal events, better sick leave, better support for a family.”
Perks and prestige
Part of the prestige of Google is all the perks associated with working there: great-looking office spaces, subsidized cafeterias, fitness centers and classes, among many others.
Another aspect that may also contribute to its prestige for software engineers, at least, is that it’s an engineering- and product-led company.
Great salaries
Of course, the excellent salaries on offer are likely to be part of your reason for applying to work at Google. Software engineers, in particular, generally receive a higher base salary and compensation than those at other major tech companies, with their expected pay 49% higher than the average salary of their peers in the US.
If all these sound exciting to you, then you’re definitely applying to the right company.
Step 1: Resume screen
The first step of Google’s recruitment process is the resume screen. Here, after you’ve submitted your application through Google’s jobs portal, or been contacted directly via email or LinkedIn, recruiters will evaluate your resume to see if your experience aligns with the open position.
Note: Google does not require cover letters and admits that they “may or may not be considered.” So, unless you have a highly untraditional profile that needs to be explained, we recommend focusing on your resume.
Thankfully, Google has already laid out its own list of tips on how to craft a great resume. We recommend you follow them. Here are the tips:
Google’s tips on crafting a resume:
- Study the job description: “Align your skills and experience with the job description. Tie your work directly to the role qualifications (and don’t forget to include data).”
- Be specific: “Be specific about projects you’ve worked on or managed. What was the outcome? How did you measure success? When in doubt, lean on the formula, “accomplished [X] as measured by [Y], by doing [Z].”
- Emphasize leadership: “If you've had a leadership role, tell us about it. How big was the team? What was the scope of your work?”
- Include coursework only if you’re a recent graduate: “If you're a recent university graduate or have limited work experience, include school-related projects or coursework that demonstrate relevant skills and knowledge.”
- Keep it concise: “We don’t have a length requirement, but concision and precision are key — so think twice before letting your resume move onto multiple pages, and take careful aim with your information.”
To learn more, take a look at our comprehensive guide: How to write a resume for Google (including 6 examples from successful Google candidates).
Alternatively, you can use one of our role-specific guides:
- Tech resume guide
- Software engineer resume guide
- Product manager resume guide
- Technical program manage resume guide
- Engineering manager resume guide
- Data science resume guide
- Machine learning engineer resume guide
Don’t forget to have a friend or family member proofread your resume before finalizing it. They’ll be able to spot grammar and formatting errors. For expert help on whether or not your resume is best suited for the position, you’ll need to get input from ex-Google interviewers.
Step 2: Recruiter call
After your resume has been approved, a recruiter will get in contact with you to schedule a call. This generally lasts 20-30 minutes.
During the call, the recruiter will have a non-technical chat with you about your background and why you are interested in the job. You should have answers prepared for questions like, “Tell me about yourself,” “Why Google?”, and “Walk me through your resume.”
The recruiter will also discuss with you how the overall interview process will work. If you have any specific questions (e.g. timeline, location, clarification about the job description), now is the time to ask.
The recruiter will be your point person for the rest of the interviews, and the best suited to answer your questions about the process. So it’s important to keep lines of communication with them open.
If all goes well, the recruiter will get back in touch with you to schedule your first interviews: the phone screens.
Step 3: Phone screen(s)
Depending on the role, you will either have one or two phone screens with your hiring manager, or a future peer of the team you’re applying to join.
These will typically last between 45 and 60 minutes each, over Google Meet. In the majority of cases, this will be a video call, but in some cases the interviewer may choose to keep their camera turned off.
We’ve researched the interview process and questions for six Google roles, so we’ll give you an idea of what to expect by role. If you’re looking for exact example questions to work with, see our guide to Google interview questions and answers.
What to expect in Google phone screens (by role):
Product managers: you’ll be asked about your background, followed by a mix of product design, estimation, and strategy questions.
Software engineers: you’ll share a Google Doc or a collaborative coding platform with your interviewer and answer data structure and algorithm questions, as well as a few behavioral questions.
Engineering managers: you’ll have a similar coding round as the software engineers, with higher-level coding questions and behavioral questions around people and project management.
Data scientists: you’ll be asked a few general background questions, as well as SQL, coding, and statistics questions, showing your work on a Google Doc or coding platform.
Technical program managers: you’ll be asked a mix of program management, technical, and leadership questions.
Account managers: you’ll be asked primarily behavioral and background questions that test your client service skills.
In some cases, you might also get an online assessment in the form of a workstyle survey. Depending on the role you're applying for, it may include role-related assessments, like a coding exercise.
Ultimately, if you’re prepared for the types of in-depth questions you’ll receive at the onsite stage, then you’ll be prepared for the initial phone screens. So let’s dive into the onsite portion, including the exact interview questions that have been reported by past candidates.
Click here to find out if you're ready for a FAANG interview.
Step 4: Onsite interviews
The longest and most daunting step of the Google interview process is the onsite interview loop. This may take place in Google’s physical offices, or via video call.
Here, you will face up to six back-to-back interview rounds that last around 45 minutes each. If you are physically onsite, one of these will take the form of an informal lunch interview with a future peer of the team you’re applying to join.
To see a breakdown of the kind of questions you're likely to face in your onsite interviews, check out our comprehensive guide to Google interview questions (with answers).
As we mentioned before, we have created in-depth guides to the interviews for top Google roles. There you’ll find a breakdown of the interview loop specific to the roles you’re applying for, plus some example questions we’ve gathered from real candidate reports on Glassdoor.
Role-specific
- How to Get a Job at Google
- Google Product Manager interview
- Google Associate Product Manager interview
- Google Product Marketing Manager interview
- Google Program Manager interview
- Google Technical Program Manager interview
- Google Software Engineer interview
- Google Engineering Manager interview
- Google Data Scientist interview
- Google Data Engineer interview
- Google Machine Learning Engineer interview
- Google Site Reliability Engineer interview
- Google L4 Engineer interview
- Google Strategy & Operations interview
- Google (Technical) Account Manager interview
Skill-specific
- Google Coding interview
- Google Code Review interview
- Google System Design interview
- 23 Google Interview Questions
Google internal and external transfers
If you're currently a Googler looking into switching roles or ladders within the company, the interview guides above will be useful as you prepare for your internal transfer application. To learn more, check out our guide to Google internal transfers.
Same goes if you're from Amazon and looking to transfer to Google. If you want to learn more about making such a career move, check out our article on how to move from Amazon to Google.
Step 5: Hiring committee
After the onsite rounds, your interviewers grade your performance using a standardized feedback form. It contains your responses to each of the questions, their feedback on your responses, and their final recommendation (e.g. "Strong no hire," "No hire," "Leaning no hire," "Leaning hire," "Hire," "Strong hire").
The feedback forms from each of your onsite interviewers are combined in a packet, which includes your resume and feedback from the initial phone screens, and it is sent to a third-party hiring committee for review.
Your recruiter will notify you when your application has progressed to this stage—all you have to do is wait.
The hiring committee is made up of a group of third-party Googlers who were not present during your interviews. Google uses this committee to make the hiring decision, rather than your interviewers, in order to remove bias from the interview process.
Overall, you’ll be assessed on the four main attributes Google looks for when hiring:
- Role-related knowledge and experience (RRK). The company wants to make sure that you have the right experience, domain expertise, and competencies for the position you're applying for. More information in this guide to Google RRK questions.
- General cognitive ability (GCA). The company wants to hire smart employees who can learn and adapt to new situations. Here your interviewer will try to understand how you solve hard problems and how you learn. More information in our guides to GCA interviews and hypothetical interview questions.
- Leadership. Google looks for a particular type of leadership called “emergent leadership.” You'll typically be working in cross-functional teams at Google, and different team members are expected to step up and lead at different times in the lifecycle of a project when their skills are needed. More information in this guide to Google leadership questions.
- Googleyness (i.e. culture fit). The company wants to make sure Google is the right environment for you. Your interviewer will check whether you naturally exhibit the company's values, including: being comfortable with ambiguity, having a bias to action, and a collaborative nature. More information in this guide to Googleyness.
Your recruiter will notify you when the hiring committee has made a decision. This typically takes one to two weeks after the onsite interview rounds. Beyond that time, if you have not received an answer, send a polite check-in to your recruiter to get more information.
There are four general responses that you may receive from Google’s hiring committee:
- You’re hired! Now you just wait to receive your offer package and go through salary negotiations.
- They want you onboard, but have to find out what team to put you in first. (More on team matching in the next section.)
- They need more information about you. One or two more interviews will be scheduled, after which the hiring committee will reconvene to make a decision.
- You get rejected. Try not to be too disappointed, many candidates get in after multiple attempts. Read our article on Google rejection and get ready to try again!
Step 6: Team-match
If you applied and interviewed for a role that is specific to a certain team at Google from the beginning, then you will likely skip the team-matching step.
Otherwise, candidates go through a separate step in order to find out which team they’ll be working for at Google. This may occur before or after the hiring committee makes its decision.
If team matching occurs after the hiring committee, the candidate’s information is passed along to teams with open headcounts, in order to find the best fit for the new hire.
If team matching occurs before the hiring committee, the information is added to the packet of interview materials that the hiring committee evaluates to make its decision.
In either case, you may have an interview scheduled to meet with members of a few different teams. Here, the recruiter will inform you of the interview and who you’ll be meeting with. We recommend that you research the teams ahead of the interview to get an idea of what questions to ask them, and what you’re most interested in.
As always, if you are unsure of any step in your specific interview process, check in with your recruiter.
Step 7: Salary negotiation
Finally, once you’ve passed each of the six steps above, you’ll receive your offer package from Google.
At this point, all that is left for you to do is negotiate your offer. Your recruiter will get in touch with you about the details, likely scheduling one final call to clarify and discuss the terms. If they have not scheduled a call, you can ask for one.
Of course, salary discussions can be difficult and a bit uncomfortable, especially if you are not used to them. Below are some tips to help you navigate your salary negotiations. And you can also get salary negotiation coaching from ex-FAANG recruiters to help you maximize your compensation.
Salary negotiation tips:
- Be polite: Remember that the person you’re negotiating with is just doing their job, and that the two of you are not enemies. You’ll get much farther in your negotiations if you approach the conversation with grace.
- Don’t give a number right away: Whenever possible, it’s better to wait until you receive an offer to start negotiating. This reduces the risk of giving a number that is lower than what the company otherwise would have paid, or giving a number that is so high that they are reluctant to interview you.
- Do your research: Have a number in mind before the conversation begins, and back it up with data. Research your position and level on Levels.fyi, ask around on professional social networking sites like Blind, factor in the cost of living where you are, and, ideally, get some input from a current Googler.
- Start high: To start the conversation, name a compensation number that is higher than your goal, and the Google negotiator will likely end up negotiating it down to a number that is closer to your original goal.
- Negotiate everything: Your offer will include more than a base salary and stock options—you also have bonuses, vacation days, location, work from home, and other aspects to consider. If the compensation won’t budge, there may be some wiggle room around the other perks.
For even more salary negotiation tips, check out our Google job offer negotiation guide. Once you’re ready to put your negotiation skills to the test, get salary negotiation coaching from ex-FAANG recruiters so you can practice with and get instant feedback from a real expert.
Once you’ve completed this step and accepted your offer, congratulations! It’s time to start your career at Google.
Are you prepared for your Google interviews?
We've coached more than 15,000 people for interviews since 2018. In our experience, practicing real interviews with experts who can give you company-specific feedback makes a huge difference.
Find a Google interview coach so you can:
- Test yourself under real interview conditions
- Get accurate feedback from a real expert
- Build your confidence
- Get company-specific insights
- Learn how to tell the right stories, better.
- Save time by focusing your preparation
Landing a job at a big tech company often results in a $50,000 per year or more increase in total compensation. In our experience, three or four coaching sessions worth ~$500 will make a significant difference in your ability to land the job. That’s an ROI of 100x!