To ace your coding interview for a software engineering job, you’ll need to understand greedy algorithms. Greedy algorithms solve optimization problems using the “greedy heuristic,” making locally optimal choices at each stage. Greedy algorithms are often intuitive and implemented more simply than other algorithms, but are not guaranteed to find globally optimal solutions.
Let’s take a look at some typical greedy algorithm questions.
5 typical greedy algorithm interview questions
-
Given the array points (balloons are represented as a 2D integer array points where points[i] = [xstart, xend] denotes a balloon whose horizontal diameter stretches between xstart and xend), return the minimum number of arrows that must be shot to burst all balloons.
-
You are given an integer array nums. You are initially positioned at the array's first index, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position. Return true if you can reach the last index, or false otherwise.
-
Given an array of strings words, return the smallest string that contains each string in words as a substring. If there are multiple valid strings of the smallest length, return any of them.
-
Given two integer arrays gas and cost, return the starting gas station's index if you can travel around the circuit once in the clockwise direction, otherwise return -1.
-
Given a set of n activities with their start and finish times, we need to select the maximum number of non-conflicting activities that can be performed by a single person, given that the person can handle only one activity at a time.
Below, we take a look at 50 greedy algorithm questions and provide you with links to high quality solutions to them.
This is an overview of what we’ll cover:
- Easy greedy algorithm interview questions
- Medium greedy algorithm interview questions
- Hard greedy algorithm interview questions
- Greedy algorithm basics
- Greedy algorithm cheat sheet
- How to prepare for a coding interview
Click here to practice coding interviews with ex-FAANG interviewers
Let's get started.
1. Easy greedy algorithm interview questions
You might be tempted to try to read all of the possible questions and memorize the solutions, but this is not feasible. Interviewers will always try to find new questions, or ones that are not available online. Instead, you should use these questions to practice the fundamental concepts of greedy algorithms.
As you consider each question, try to replicate the conditions you’ll encounter in your interview. Begin by writing your own solution without external resources in a fixed amount of time.
If you get stuck, go ahead and look at the solution, but then try the next one alone again. Don’t get stuck in a loop of reading as many solutions as possible! We’ve analysed dozens of questions and selected ones that are commonly asked and have clear and high quality answers.
Here are some of the easiest questions you might get asked in a coding interview. These questions are often asked during the “phone screen” stage, so you should be comfortable answering them without being able to write code or use a whiteboard.
Question 1: Assign cookies
- Text guide (Medium/Fatboy Slim)
- Video guide (Nick White)
- Video guide (Kevin Naughton Jr.)
- Code example (fabrizio)
Question 2: Can place flowers
- Text guide (dilyar85)
- Video guide (NeetCode)
- Video guide (Nideesh Terapalli)
- Code example (soumyadeep2007)
Question 3: Lemonade change
- Text guide (Tutorial Cup)
- Video guide (Nick White)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 4: Partition array into three parts with equal sum
- Text guide (walkccc)
- Video guide (Ren Zhang)
- Code example (rock)
Question 5: Split a string in balanced strings
- Text guide (Medium/Rahul Gupta)
- Video guide (Kevin Naughton Jr.)
- Code example (dnuang)
Question 6: Maximum units on a truck
- Text guide (Dev.to/seanpgallivan)
- Video guide (Naresh Gupta)
- Code example (rock)
Question 7: Minimum moves to convert string
- Text guide (TechieDelight)
- Video guide (Programming Live with Larry)
- Code example (pollux1997)
2. Medium greedy algorithm interview questions
Here are some moderate-level questions that are often asked in a video call or onsite interview. You should be prepared to write code or sketch out the solutions on a whiteboard if asked.
Question 8: Jump game
- Text guide (Learnbay)
- Video guide (NeetCode)
- Code example (1337beef)
Question 9: Gas station
- Text guide (After Academy)
- Video guide (NeetCode)
- Code example (daxianji007)
Question 10: Jump game II
- Text guide (Medium/Nerd For Tech)
- Video guide (NeetCode)
- Code example (Cheng Zhang)
Question 11: Remove duplicate letters
- Text guide (Zirui)
- Video guide (Naresh Gupta)
- Code example (lixx2100)
Question 12: Wiggle subsequence
- Text guide (LeetCode)
- Video guide (probability_coding_is_fun_is_1)
- Code example (TenffY)
Question 13: Remove K digits
- Text guide (OpenGenus)
- Video guide (Nick White)
- Code example (kevinlai)
Question 14: Queue reconstruction by height
- Text guide (Medium/codeandnotes)
- Video guide (TECH DOSE)
- Code example (YJL1228)
Question 15: Non-overlapping intervals
- Text guide (Medium/The Startup)
- Video guide (NeetCode)
- Video guide (TECH DOSE)
- Code example (WangQiuc)
Question 16: Minimum number of arrows to burst balloons
- Text guide (Medium/Rohith)
- Video guide (Naresh Gupta)
- Code example (Joshua924)
Question 17: Task scheduler
- Text guide (Medium/Shymmy W. Garcia)
- Video guide (Naresh Gupta)
- Code example (g27as)
Question 18: Maximum length of pair chain
- Text guide (GeeksForGeeks)
- Video guide (Coding Gist)
- Video guide (TECH DOSE)
- Code example (yuxiong)
Question 19: Dota2 senate
- Text guide (FatalErrors)
- Code example (caihao0727mail)
Question 20: Split array into consecutive subsequences
- Text guide (junhaow)
- Video guide (Nideesh Terapalli)
- Code example (fun4LeetCode)
Question 21: Maximum swap
- Text guide (sugarac)
- Video guide (Algorithms Illustrator)
- Code example (joe53211)
Question 22: Monotone increasing digits
- Text guide (zhenyu0519)
- Video guide (Geek gang)
- Code example (Zee)
Question 23: Partition labels
- Text guide (algorithmsandme)
- Text guide (LeetCode)
- Video guide (NeetCode)
- Code example (DBabichev)
Question 24: Reorganize string
- Text guide (zhenyu0519)
- Video guide (Kevin Naughton Jr.)
- Code example (zestypanda)
Question 25: Increasing triplet subsequence
- Text guide (Medium/xiao mei)
- Video guide (Algorithms Made Easy)
- Code example (sim5)
Question 26: Max increase to keep city skyline
- Text guide (Tutorialspoint)
- Video guide (Nick White)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 27: Score after flipping matrix
- Text guide (Medium/Anj)
- Video guide (Leet Terps)
- Code example (faangboy)
Question 28: Hand of straights
- Text guide (Massive Algorithms)
- Video guide (NeetCode)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 29: Minimum add to make parentheses valid
- Text guide (Helloacm)
- Video guide (happygirlzt)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 30: Advantage shuffle
- Text guide (LeetCode)
- Text guide (Dev.to/seanpgallivan)
- Video guide (Algorithms Made Easy)
- Code example (caraxin)
Question 31: Minimum increment to make array unique
- Text guide (Tutorialspoint)
- Video guide (Happy Coding)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 32: Boats to save people
- Text guide (Massive Algorithms)
- Video guide (Kevin Naughton Jr.)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 33: Smallest range II
- Text guide (Medium/Jimmy Shen)
- Video guide (Algorithms Made Easy)
- Code example (dim_sum)
Question 34: Delete columns to make sorted II
- Text guide (Programmerall)
- Video guide (Hunter Macias)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 35: Bag of tokens
- Text guide (Medium/Glyn Liu)
- Video guide (Kevin Naughton Jr.)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 36: String without AAA or BBB
- Text guide (LeetCode)
- Video guide (happygirlzt)
- Code example (votrubac)
Question 37: Array of doubled pairs
- Text guide (hiepit)
- Video guide (Coding Decoded)
- Code example (Walkccc)
3. Hard greedy algorithm interview questions
Similar to the medium section, these more difficult questions may be asked in an onsite or video call interview. You will likely be given more time if you are expected to create a full solution.
Question 38: Candy
- Text guide (LeetCode)
- Video guide (Algorithms Made Easy)
- Code example (meng789987)
Question 39: Create maximum number
- Text guide (Medium/dume0011)
- Code example (dietpepsi)
Question 40: Patching array
- Text guide (HackingNote)
- Video guide (Timothy H Chang)
- Code example (StefanPochmann)
Question 41: Smallest range covering elements from K lists
- Text guide (LeetCode)
- Video guide (IDeserve)
- Code example (awice)
Question 42: Minimum cost to hire K workers
- Text guide (shengqianliu)
- Video guide (Shiran Afergan)
- Video guide (AlgoCademy)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 43: IPO
- Text guide (Massive algorithms)
- Video guide (Imran Sarwar)
- Video guide (Ren Zhang)
- Code example (shawngao)
Question 44: Set intersection size at least two
- Text guide (Titanwolf)
- Code example (fun4LeetCode)
Question 45: Course schedule III
- Text guide (Dev.to/seanpgallivan)
- Video guide (Timothy H Chang)
- Code example (KakaHiguain)
Question 46: Couples holding hands
- Text guide (Medium/Jolyon)
- Video guide (Arpan Pathak)
- Code example (LeetCode)
Question 47: Minimum number of refueling stops
- Text guide (Dev.to/seanpgallivan)
- Video guide (Algorithms Made Easy)
- Code example (chipbk10)
Question 48: Longest chunked palindrome decomposition
- Text guide (Tutorialspoint)
- Code example (lee215)
Question 49: Stamping the sequence
- Text guide (Dev.to/seanpgallivan)
- Video guide (Algorithms Made Easy)
- Code example (FLAGbigoffer)
Question 50: Minimum number of taps to open to water a garden
- Text guide (Medium/Kostya)
- Video guide (Tony Teaches)
- Code example (BlueCamel)
4. Greedy algorithms basics
In order to crack questions about greedy algorithms, you’ll need to have a strong understanding of the technique, how it works, and when to use it.
4.1 What are greedy algorithms?
A greedy algorithm is an algorithmic paradigm that finds the optimal solution to a problem by breaking the problem down into smaller (local) parts and finding the best solution for each of these parts.
Greedy algorithms are best applied to problems with the following two properties:
- The optimal solution to the problem can build on the optimal solutions to smaller pieces of the problem. This property is known as having an optimal substructure.
- The global optimum can be reached by choosing the local optimum of each sub-problem without the need to consider future implications. This is called the greedy choice property.
An activity selection problem can be used to demonstrate these properties. Suppose we have the following options of activities to complete for the day and the optimal solution is to complete as many activities as possible:
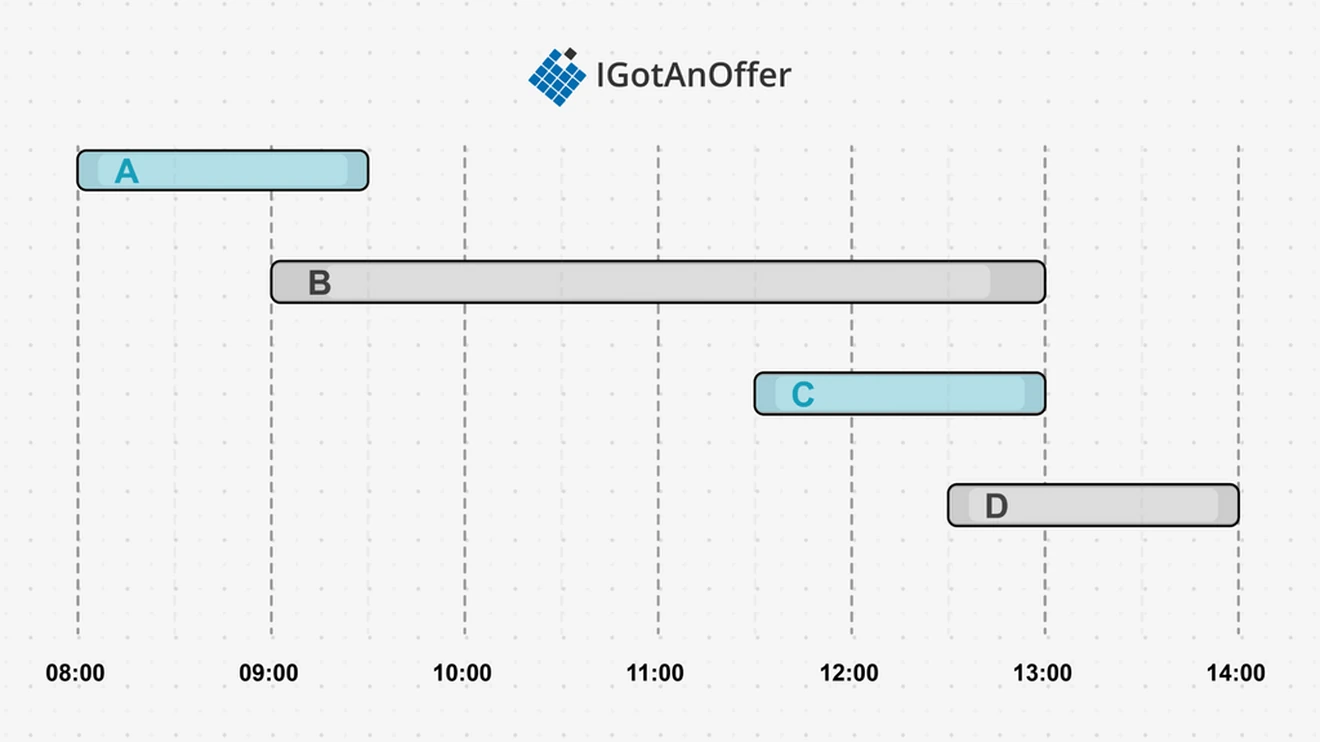
The problem can be broken into smaller parts, for example, choosing the best activity to complete first and the remaining time become sub-problems. The best activity to complete first is the one that will finish first. Activity A finishes first at 9:30, so it is the local optimum, and the time range of 9:30 to 14:00 is the new sub-problem to solve.
The B activity falls outside this sub-problem window, so it is removed from the possible solutions set. This makes C the new local optimal, and the global problem is solved with A and C. A total of two activities are completed.
Selecting the correct heuristic for the greedy algorithm to base its choice on is critical to the functioning of the greedy algorithm. If we break the greedy choice property by using a heuristic for the local best that does not lead to a global best, then we will not find an optimal solution. For example, in the diagram below, if an activity is chosen based on having the shortest timespan, only one activity will be completed, although it is possible to complete two:
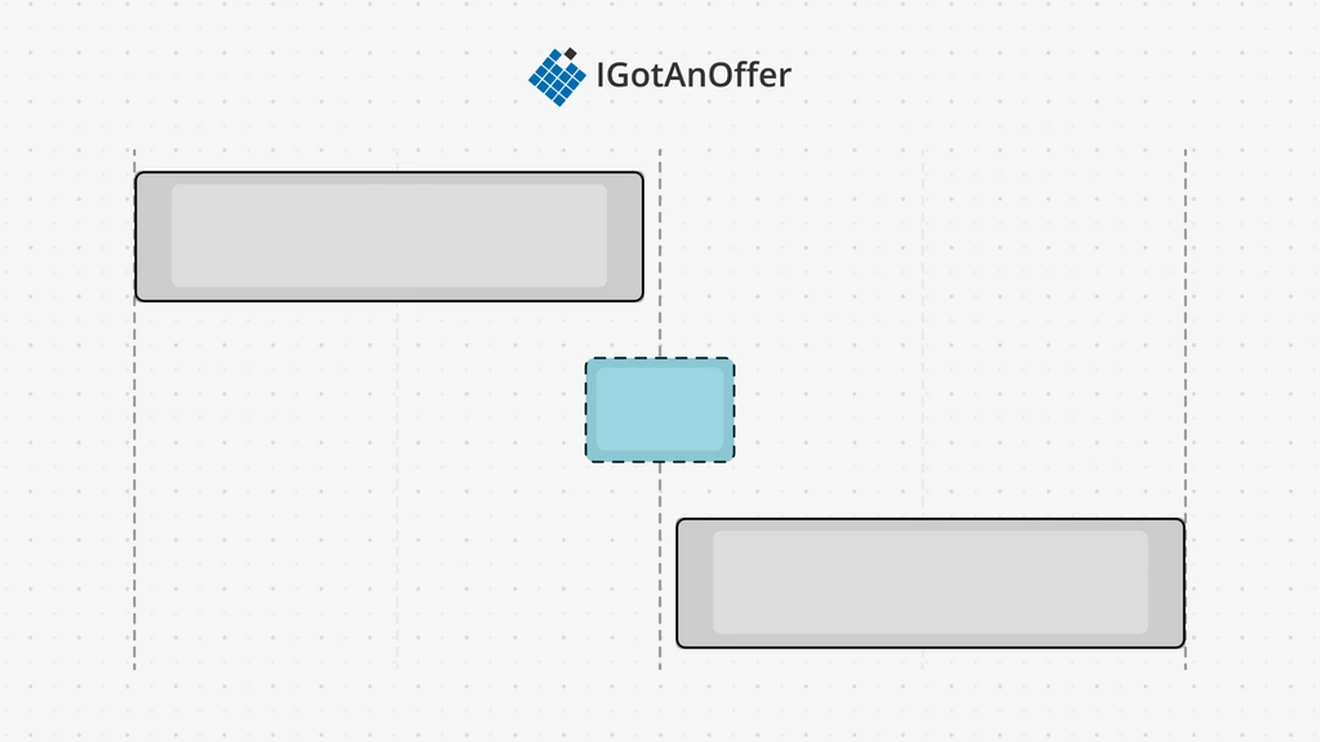
Because the highlighted activity requires the least time, it will be chosen. But this will remove the other two activities from the solution set. Instead, the "finish-first heuristic" of our first example would have selected the two unhighlighted activities.
Therefore, greedy algorithms can lead to non-optimal solutions. The only way to prove optimal solutions is to prove the greedy choice property, which is not always possible.
4.1.1 Use cases for greedy algorithms
Some of the problems greedy algorithms can be applied to are:
- Activity selection problem
- Shortest / longest path problems
- Decision tree learning
- Huffman encoding
- Minimum spanning tree problems
- Fractional knapsack problem
- Job scheduling in operating systems
- Traveling salesman problem
- K-centers problem
- Graph coloring
4.1.2 Example implementation
Implementations of greedy algorithms are similar to depth-first searching (DFS), except that only the single best solution is expanded in a greedy algorithm, whereas DFS will expand all the children of a node.
For the activities problem, this gives the following implementation:
The first part defines an activity class and its less than (<) operator so that it can be used in a sort later. The optimal_activities function makes a copy of the original list so as not to override it, and then sorts it to place the best activities first. The loop takes the best available activity that does not start before the last chosen activity’s end time. Else it becomes part of the solution, since it is the local optimal. Since this solution only has a single loop, it has a time complexity of O(n) plus the complexity for sorting.
4.1.3 How greedy algorithms compare to other algorithms
The most basic alternative to a greedy algorithm is a brute-force algorithm, which looks at all the possible solutions to a problem. But using a brute-force approach in our activity selection example will have a time complexity of O(n!).
Greedy algorithms are different from divide-and-conquer algorithms, but are related in terms of their need to solve a smaller sub-problem. Divide-and-conquer algorithms require an optimal substructure (but not the greedy choice property). Greedy algorithms can be simpler to implement than divide-and-conquer, as you only need to make a single choice at any given step.
Greedy algorithms tend to use less space than dynamic programming solutions, but dynamic programming can return all the optimal solutions, not just one. Dynamic programming properties (optimal substructures) are easier to prove than the greedy choice property.
The greedy choice property means that a greedy algorithm never looks back at its past solutions. In contrast, a backtracking algorithm will reconsider past solutions whenever it hits a dead end.
Greedy algorithms are a good choice when they are guaranteed to find the optimal solution to a problem, or at least a good enough solution. Their main benefit over other algorithms is speed and simplicity.
Need a boost in your career as a software engineer?
If you want to improve your skills as an engineer or leader, tackle an issue at work, get promoted, or understand the next steps to take in your career, book a session with one of our software engineering coaches.
5. Greedy algorithms cheat sheet
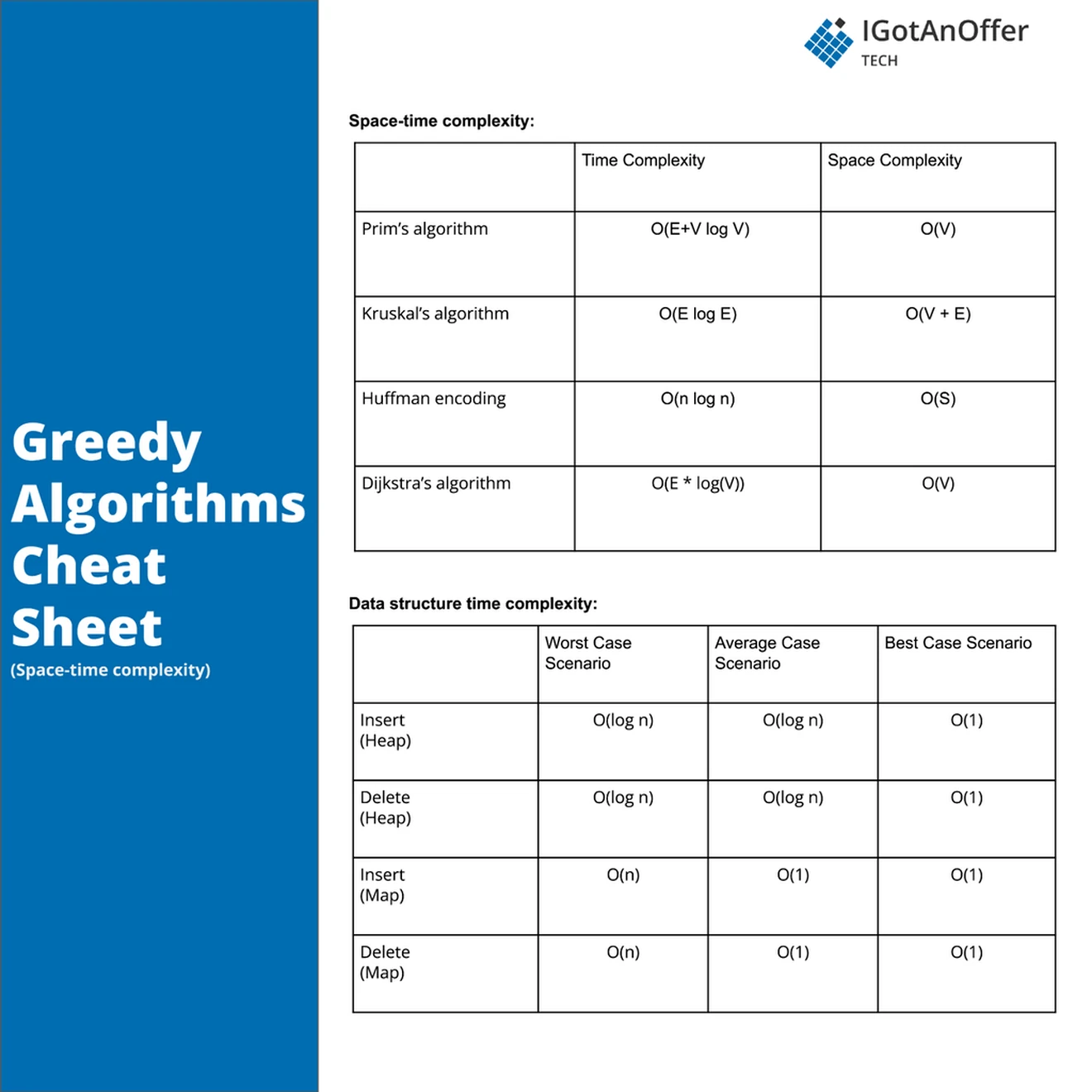
You can download the cheat sheet here.
5.1 Related algorithms and techniques
5.2 Cheat sheet explained
The cheat sheet above is a summary of information you might need to know for an interview, but it’s usually not enough to simply memorize it. Instead, aim to understand each result so that you can give the answer in context.
The cheat sheet is broken into time complexity and space complexity (the processing time and memory requirements for greedy algorithms). Greedy algorithms are related to several data structures, which are also included in the cheat sheet.
For more information about time and space requirements of different algorithms, read our complete guide to big-O notation and complexity analysis.
5.2.1 Time complexity
In the implementation of our example activity selection problem, a single loop and a sort gave our greedy algorithm a time complexity of O(n log n). In general, greedy algorithms need to evaluate the local optimum and will sort the solution space, for a time complexity of O(n log n) outside a loop. Alternatively, a greedy algorithm can use a priority queue like a heap, with a time complexity of O(log n), in a loop, with a time complexity of O(n log n).
The greedy implementation of Huffman coding is an example of using a heap to store the weight of each encoding symbol to determine its final bit string. Each symbol needs to be iterated over, log(n), and each iteration will insert or update the heap, O(log n). This gives a total time complexity of O(n log n).
Prim’s algorithm is another example of a greedy algorithm using a heap to find a minimum spanning tree (MST) for a weighted undirected graph. Prim’s algorithm does this by keeping a heap of vertices to add to the MST next, O(log |V|) to add, update or pop from the heap, while continuously looping over the edges of the smallest vertex in the heap, O(|E|). The vertices connected to these edges are only added to the heap if they are not already in MST, O(|V|), for a total time complexity of O((|V| +|E|) log |V|).
5.2.2 Space complexity
Our example activity selection problem implementation only has a copy of the original activities list, O(n), and a solutions list that will at worst contain all the activities, O(n). This gives it a total space complexity of O(n). In general, using an extra sorted list or a heap will only take n extra space for a space complexity of O(n).
The Huffman coding heap will store the weights of each distinct symbol (S). If every symbol is unique, in the worst case, the heap will have a total of |S| leaves, and therefore the heap can have 2|S|-1 nodes. This gives a space complexity of O(|S|).
Prim’s algorithm will contain all the vertices in the MST when the heap is exhausted – |V|. At worst, all the vertices may be added to the heap on the first expansion, to give the heap a max size of |V|-1. This gives a total space complexity of O(|V|).
5.2.3 Related algorithms and data structures: sorting algorithms and heaps
Greedy algorithms need a way to find the local optimum, which is easily done when the solution space is sorted or in a priority queue. On average, sorting algorithms perform at O(n log n) time. Choosing the wrong sorting algorithm for the scenario, like Quicksort, can degrade the performance to O(n^2).
Heaps are a good choice for priority queues, and the operations most likely to be used have a time complexity of O(log n). However, interaction with the heap is likely to happen within a loop over all the elements, to give the same performance of sorting at O(n log n).
6. How to prepare for a coding interview
6.1 Practice on your own
Before you start practicing interviews, you’ll want to make sure you have a strong understanding of not only greedy algorithms but also the rest of the relevant algorithms and data structures. You’ll also want to start working through lots of coding problems.
Check out the guides below for lists of questions organized by difficulty level, links to high-quality answers, and cheat sheets.
Algorithm guides
- Breadth-first search
- Depth-first search
- Binary search
- Sorting
- Dynamic programming
- Backtracking
- Divide and conquer
Data structure guides
- Arrays
- Strings
- Linked lists
- Stacks and Queues
- Trees
- Graphs
- Maps
- Heap
- Coding interview examples (with solutions)
To get used to an interview situation, where you’ll have to code on a whiteboard, we recommend solving the problems in the guides above on a piece of paper or google doc.
6.2 Practice with others
However, sooner or later you’re probably going to want some expert interventions and feedback to really improve your coding interview skills.
That’s why we recommend practicing with ex-interviewers from top tech companies. If you know a software engineer who has experience running interviews at a big tech company, then that's fantastic. But for most of us, it's tough to find the right connections to make this happen. And it might also be difficult to practice multiple hours with that person unless you know them really well.
Here's the good news. We've already made the connections for you. We’ve created a coaching service where you can practice 1-on-1 with ex-interviewers from leading tech companies. Learn more and start scheduling sessions today.