Today, we're going to cover everything you need to know to prepare for your Uber data scientist interview.
The Uber interview process is challenging. You're expected to demonstrate both outstanding technical expertise in SQL, Python, and statistics, and strong business intuition to tackle complex marketplace problems. Plus, you'll need to show your ability to design experiments and leverage data to drive product decisions at scale.
The good news? With the right preparation, you can significantly improve your chances of landing that data scientist role at Uber.
In this guide, we've gathered all the resources you need to ace your Uber data scientist interviews: real candidate experiences, information from official sources, plus expert advice from our expert coaches, who are former data scientists and interviewers at companies like Uber and other top tech firms.
You’ll also find below a detailed breakdown of the interview process and some sample questions—everything you need to walk into each round with confidence.
- Role and salary
- Interview process and timeline
- Example interview questions
- Interviewing tips
- Preparation plan
Click here to practice 1-on-1 with data science interviewers.
1. Uber data scientist role and salary ↑
Before we cover your data scientist interviews at Uber, let's take a quick look at the role itself.
1.1 What does an Uber data scientist do?
As a data scientist at Uber, you'll be responsible for using data to drive key product and business decisions across one of the world's largest marketplace platforms. Your work will directly impact millions of riders and drivers daily through experimentation, analytics, and machine learning.
Data scientists at Uber work on rigorous experiments, real-time analytics, and dynamic marketplace optimization. You'll process and analyze petabyte-scale datasets to improve algorithms that manage supply and demand across hundreds of cities. Your insights will shape how over 30 million Uber trips happen each day.
Uber has data science teams across Mobility (ride-sharing), Delivery (Uber Eats), Freight, and Platform. Within these organizations, you could work on areas like growth, marketplace dynamics, pricing and incentives, driver and rider experiences, or product analytics.
Core competencies for the role include:
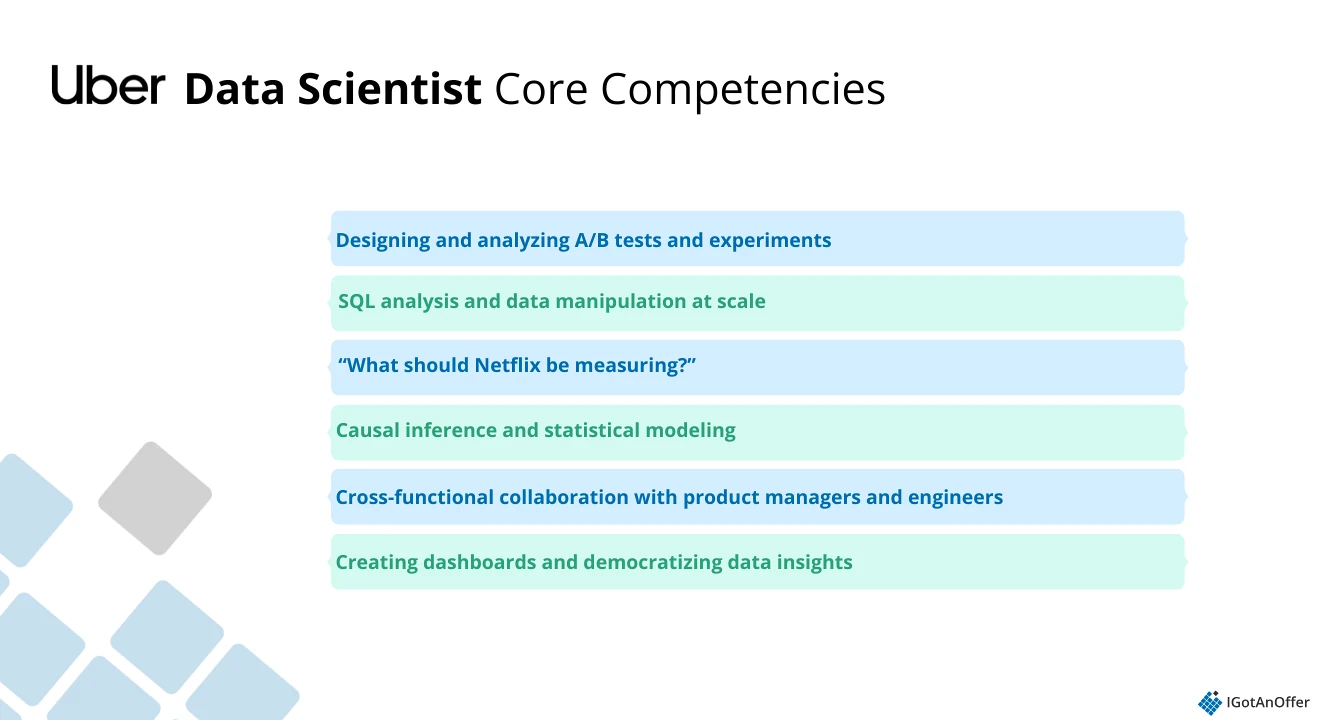
The role at Uber differs from traditional data science positions because it centers on product analytics rather than machine learning. Data scientists work more like product analysts with strong technical skills, which explains why a former Uber Applied Scientist described the position as essentially a product analyst role.
This alignment exists because the work revolves around SQL analysis, experimentation, and causal inference. As a result, the role remains firmly focused on product analytics, while Applied Scientists and Machine Learning Engineers handle the development of advanced machine learning models.
What skills does an Uber data scientist need?
An analysis of data scientist job postings at Uber shows that the company typically asks for three basic requirements:
- A bachelor's degree in statistics, mathematics, economics, computer science, or a related field (or equivalent practical experience)
- At least 3 years of experience in A/B testing, exploratory data analysis, and statistical analysis
- Proficiency in SQL and Python, or R
Additionally, Uber looks for candidates with experience in experimental design and causal inference, strong communication skills to present findings to non-technical stakeholders, business intuition to identify opportunities and frame problems, and the ability to work with large-scale datasets using tools like Hive, Presto, or Spark.
1.2 How much does an Uber data scientist make?
Here's the average salary and compensation rates for the different data scientist levels at Uber, based on reported data from Levels.fyi. Compensation mainly depends on two key factors:
- Location: Salaries are adjusted for cost-of-living.
- Level: Both base salary and total compensation go up with each data scientist level.
Uber data scientist levels and their average total yearly compensation (United States):
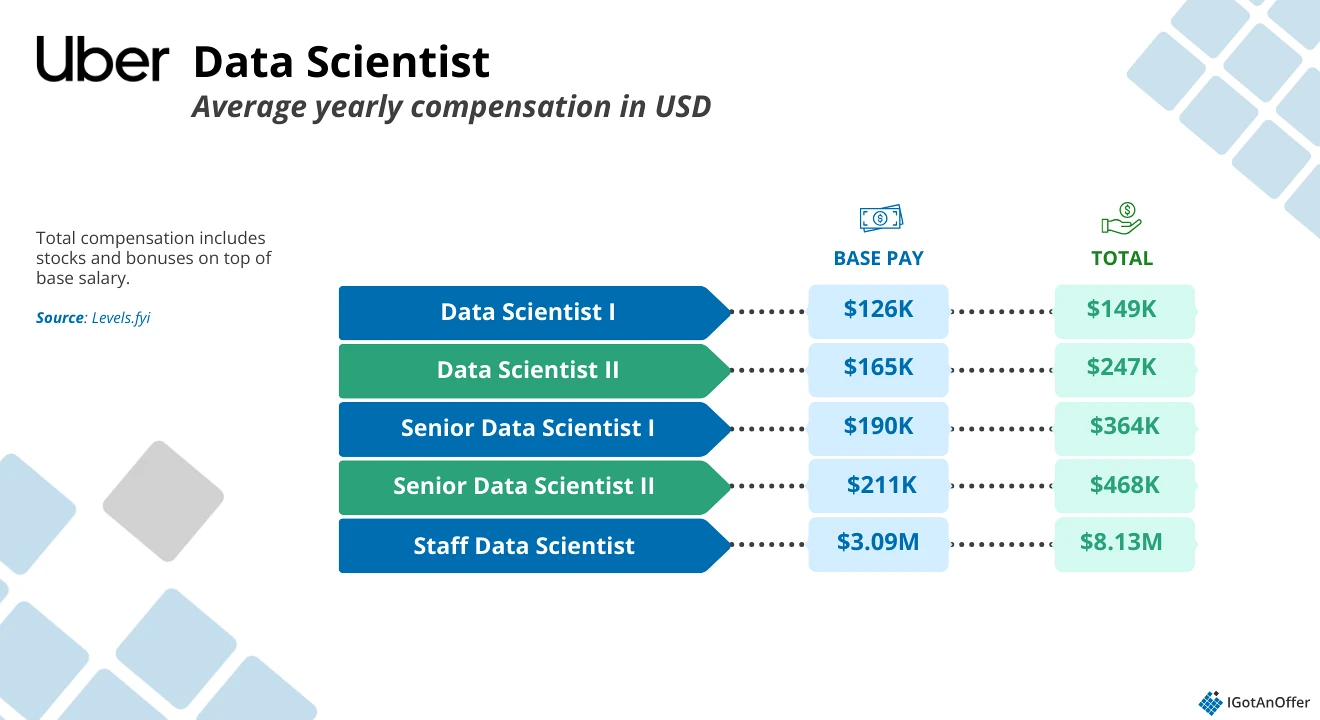
If you're unsure what level you're being considered for, ask your recruiter.
Ultimately, how you do in your interviews will determine what level you're offered. That's why hiring one of our Uber data scientist interview coaches can provide such a significant return on investment.
And remember, compensation packages are always negotiable. So, if you do get an offer, don't be afraid to ask for more. If you need help with salary negotiation, consider booking a salary negotiation coaching session with one of our experts to give yourself a leg up.
2. Uber data scientist interview process and timeline ↑
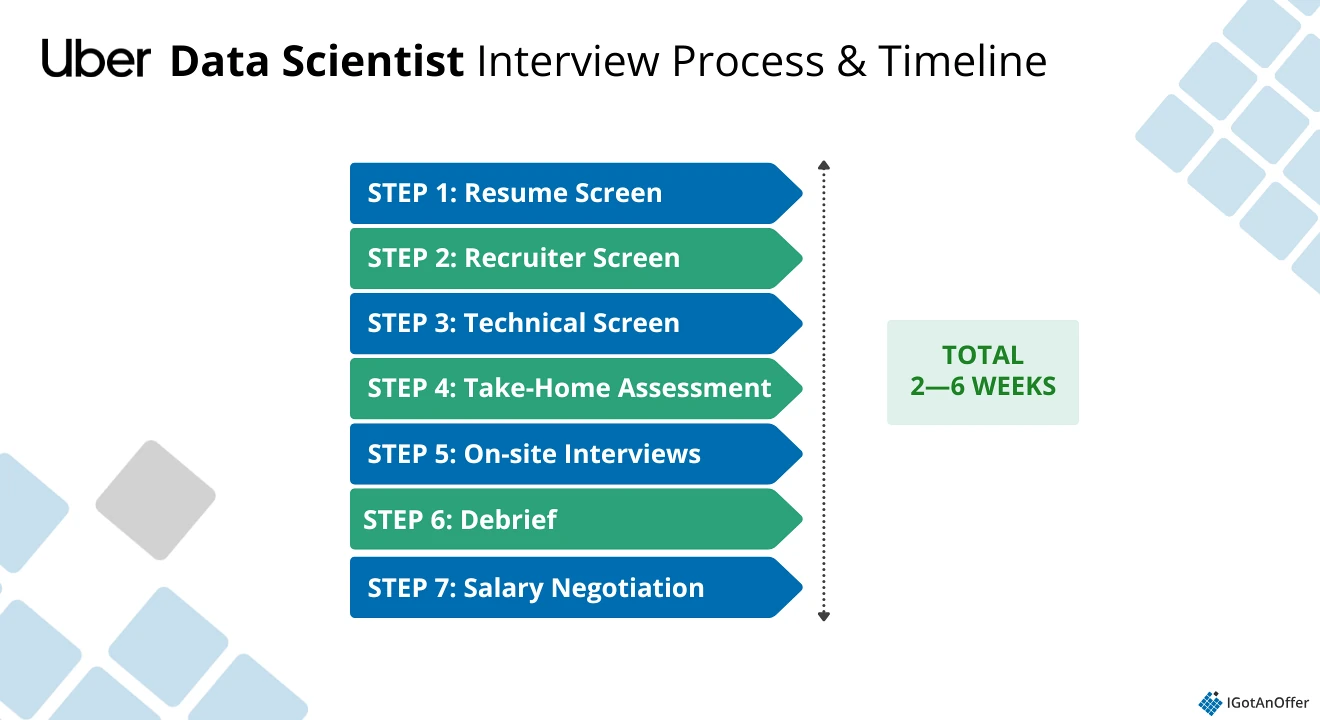
The full Uber interview process for the data scientist role typically takes 2 to 6 weeks from your initial application to when you receive an offer. Of course, the timeline can vary depending on the particular location and team for which you're applying.
Here's a quick overview of the steps you'll take along the way:
- Resume screen
- Recruiter screen
- Technical screen
- Take-home assessment (occasionally)
- On-site interviews (4-6 rounds)
- Debrief
- Salary negotiation
Let's take a look at each step in detail.
2.1 Resume screen
This is a very competitive part of your Uber application process. You'll want to make sure your resume highlights your data science experience and matches the position you're applying for.
Take a look at our data science resume guide to see which kinds of resumes get noticed and learn how to tailor your resume to data science positions.
If you're looking for expert feedback, you can also get help on your resume from one of our ex-FAANG recruiters, who will cover what achievements to focus on (or ignore), how to fine-tune your bullet points, and more.
2.2 Recruiter screen
In most cases, you'll start your interview process with Uber by talking to an HR recruiter on the phone. This is typically a 30 to 45-minute conversation where the recruiter looks to confirm that you've got a chance of getting the job at all.
Be prepared to explain your background and why you're a good fit at Uber. You should expect typical behavioral and resume questions like "Tell me about yourself" or "Why Uber?"
Check out our guide to behavioral interview questions for tips on how to answer these types of questions confidently.
If you get past this first HR screen, the recruiter will then help schedule your next rounds of screening. Former Uber EM and coach Ketki’s advice is to leverage the guidance of your recruiter at this stage so you know exactly how to prepare for each round.
“The process is designed to ensure you’re not caught off guard, so focus on aligning your preparation with those expectations. Take time to understand the purpose of each round and prepare accordingly, targeting the skills and competencies being evaluated,” she says.
Note: Unlike some other roles at Uber, data scientist positions typically don't include an online assessment stage. Your interview process will move directly from the recruiter screen to technical interviews.
2.3 Technical screen
This is a critical 45 to 60-minute assessment that combines live coding with statistical concept questions. You'll typically spend 30 minutes on SQL and Python coding challenges, followed by 15 minutes on A/B testing and statistics questions.
The interview is divided into two main sections:
- SQL portion
- Data manipulation problems with joins, aggregations, and window functions
- Questions requiring PARTITION BY, LAG/LEAD functions, and TIMESTAMPDIFF
- Medium difficulty level, heavily focused on window functions (according to Glassdoor candidates)
- Statistics portion
- A/B testing fundamentals: designing experiments, determining sample size
- Handling experimental challenges like network effects
- Uber-specific scenarios: analyzing surge pricing data or optimizing driver incentives
This technical screen is conducted on platforms like CoderPad or CodeSignal, so you'll need to be comfortable coding in a live, interactive environment without access to external resources.
2.4 Take-home assessment (occasionally)
Some candidates report receiving a take-home assignment, typically due one week after it's assigned. This assessment usually contains three sections and focuses on hands-on data analysis using real Uber data scenarios.
You might be asked to perform exploratory data analysis, create visualizations, build predictive models, or conduct statistical analysis on datasets related to rides, drivers, or marketplace dynamics.
2.5 On-site interviews
The comprehensive onsite consists of 4 to 6 rounds, each lasting 45 to 60 minutes. These interviews can be conducted virtually or in person at an Uber office. Here's what to expect:
- SQL/Coding rounds (2 interviews)
- Product case/Analytics round (1 interview)
- Statistics/A/B Testing round (1 interview)
- Machine Learning round (0-1 interview, depending on role)
- Behavioral round (1 interview)
SQL / coding rounds (2 interviews): Live coding exercises that evaluate your ability to manipulate and analyze data. You'll write queries to extract insights from complex datasets, similar to the technical screen but with increased difficulty.
Product case / analytics round (1 interview): You'll analyze ambiguous business scenarios and demonstrate your analytical thinking. Common topics include metric definition, root cause analysis, opportunity sizing, and marketplace optimization. For example, you might be asked to investigate why rider retention dropped or to design KPIs for a new driver incentive program.
Statistics and A/B testing round (1 interview): Deep dive into experimental design, causal inference, and statistical concepts. This may involve discussing regression models, A/B testing methodology, handling imbalanced datasets, or addressing network effects in experiments.
Machine learning round (0-1 interview, depending on role): Some positions include questions on ML algorithms, model evaluation, feature engineering, and practical applications of machine learning to Uber's business problems.
Behavioral round (1 interview): Questions about your past experiences, collaboration style, and cultural fit. Interviewers assess your ability to work cross-functionally, handle conflicts, and align with Uber's values.
Throughout the onsite, interviewers evaluate your technical competence, analytical thinking, business intuition, communication skills, and cultural fit with Uber's data-driven, customer-focused culture.
2.6 Debrief
Once you've completed all of your interviews, a hiring committee will hold a "debrief" to discuss your application.
A "debrief" is a meeting where your recruiter and all of your onsite interviewers come together to decide if you'll be given an offer. More specifically, this meeting includes all of the people you met during interviews, in addition to your recruiter.
During the meeting, all of these people work together to make the decision collectively. By the end of the meeting, they will come to a "hire" or "no hire" decision. Sometimes, the candidate's level is also decided during their discussion.
2.7 Salary negotiation
Finally, once you’ve passed each of the six steps above, you’ll receive your offer package from Uber.
At this point, all that is left for you to do is negotiate your offer. Your recruiter will get in touch with you about the details, likely scheduling one final call to clarify and discuss the terms. If they have not scheduled a call, you can ask for one.
Of course, salary discussions can be difficult and a bit uncomfortable, especially if you are not used to them. Below are some tips to help you navigate your salary negotiations.
Salary negotiation tips:
- Be polite: Remember that the person you’re negotiating with is just doing their job, and that the two of you are not enemies. You’ll get much farther in your negotiations if you approach the conversation with grace.
- Don’t give a number right away: Whenever possible, it’s better to wait until you receive an offer to start negotiating. This reduces the risk of giving a number that is lower than what the company otherwise would have paid, or giving a number that is so high that they are reluctant to interview you.
- Do your research: Have a number in mind before the conversation begins, and back it up with data. Research your position and level on Levels.fyi, ask around on professional social networking sites like Blind, factor in the cost of living where you are, and, ideally, get some input from a current Uber employee.
- Start high: To start the conversation, name a compensation number that is higher than your goal, and the Uber negotiator will likely end up negotiating it down to a number that is closer to your original goal.
- Negotiate everything: Your offer will include more than a base salary and stock options. You also have bonuses, vacation days, location, work from home, and other aspects to consider. If the salary won’t budge, there may be some wiggle room around the other perks.
Check out our video on 10 rules of salary negotiation for more tips.
Practice what you’ve learned before the actual negotiation. Book a salary negotiation coaching session with expert recruiters and negotiators to help you maximize your compensation.
Once you’ve completed this step and accepted your offer, congratulations! It’s time to start your career at Uber.
3. Uber data scientist example questions ↑
In this section, we'll provide example questions for each type of interview round. The questions come from real Uber data scientist interviews reported on Glassdoor.
The questions we'll list in the next few sections are typical data scientist interview questions and a few that were reported specifically for Uber data scientist interviews. We've categorized the questions and changed the grammar and phrasing in some places to make the questions easier to understand.
Interview question categories covered:
- Technical questions (SQL, Python/Scripting, Data Structures & Algorithms)
- Analytical execution questions
- Product questions (Product sense, Product metrics, Marketplace economics)
- Machine learning questions
- Statistics questions
- Experimentation & causal inference questions (A/B testing, Causal inference/experiment design)
- Research & applied analytics questions
- Data quality / governance questions
- Time series & forecasting questions
- Behavioral questions
Let's start with the technical questions, which form the foundation of Uber's data scientist interviews.
3.1 Technical questions ↑
At Uber, data drives a lot of decisions, and technical questions in interviews reflect that reality. So in your interview, you’ll be solving the same problems Uber’s data scientists tackle daily: understanding rider behavior, spotting patterns in driver activity, and measuring the impact of experiments.
The first focus area is SQL, the backbone of these analyses, where the questions mirror real-world scenarios and challenge you to think about data across time, sequences, and cohorts.
3.1.1 SQL
Every day, data scientists at Uber write queries to understand rider behavior, analyze driver patterns, optimize pricing algorithms, and measure experiment results. The SQL questions you'll face mirror the actual analyses Uber data scientists perform.
Expect questions that require sophisticated window functions to calculate metrics like rider retention cohorts, driver lifetime value, or time-based patterns in marketplace behavior.
Uber's emphasis on window functions like PARTITION BY, LAG, LEAD, and ROW_NUMBER reflects the temporal nature of their data: every trip has a timestamp, every driver has a sequence of rides. The ability to understand patterns over time is critical to marketplace optimization.
These are the exact queries data scientists write to answer questions like 'How many riders take their second trip within 7 days?' or 'What's the average time between completed trips for active drivers?'
Example SQL questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Explain JOINs to a 10-year-old.
- What database systems have you built with MySQL?
- Write SQL to detect fraud for drivers.
- Write a query to get the distribution of total push notifications before a user converts.
- Write a query to obtain the third transaction of every user. Output the user id, spend, and transaction date.
- Write a query to find out how much time, in minutes (rounded down), each plane spent in the air each day.
- Given a table of Uber transactions, write a query to find the number of customers that signed up in January 2020 and had a combined sending and receiving volume greater than $100 in their first 30 days.
- As a data analyst at Uber, report the latest metrics for specific groups of Uber users. Write a query to calculate the average delay between the day of user sign-up and the day of their second ride for "in-the-moment" users who create their account the same day they book their first ride.
- Given a table of rides with mileage and business purpose, find the top 3 business purpose categories by total mileage.
- For each service (Uber Ride, Uber Eats, Uber Freight), calculate the percentage of incomplete orders along with the percentage of revenue loss from incomplete orders relative to total revenue.
3.1.2 Python/Scripting
Python coding at Uber tests your ability to manipulate data and implement logic efficiently. Unlike software engineering roles that emphasize complex algorithms and system design, data science Python questions focus on the kinds of data transformations and calculations you'll perform regularly.
You'll use pandas to clean datasets, implement business logic to categorize transactions, or write functions to calculate custom metrics. The questions evaluate whether you can think programmatically about data problems.
Interviewers care more about whether your code is readable and gets the right answer than whether it's perfectly optimized.
Example Python questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Sort a list and print the result in Python.
- Write production-ready code to find all combinations of numbers in a list that sum to 8.
- Build a text wrapper that splits a long sentence at spaces based on a character limit.
- Write code to simulate the roll of a die using only a continuous uniform random generator.
- Given a Bernoulli-trial generator, write a function that returns a sample from a normal distribution.
- How would you calculate the square root of x without using built-in sqrt?
3.1.3 Data structures & algorithms (DSA)
Algorithmic questions are less common here than at software engineering roles, but they do appear occasionally, especially for senior positions.
When they come up, they usually connect to real Uber problems: How do you efficiently match thousands of ride requests to available drivers? What's the best algorithm for routing UberPool pickups?
These questions test your ability to think systematically about optimization problems and understand trade-offs between different approaches. Even if you won't build these systems yourself, understanding how they work helps you design better experiments and interpret results.
Example DSA questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Calculate the square root of an integer.
- How would you best match a ride request to a driver?
- What algorithm would you use to determine whether a driver accepts or rejects a request?
- Which supervised ML algorithm would you pick for the driver-request matching problem?
- How do you compare the results of two algorithms?
For more guidance on SQL, Python, and DSA questions, check out our coding interview guide.
3.2 Analytical execution questions ↑
These questions test how you investigate unclear business problems and find actionable insights. At Uber, data scientists figure out what questions to ask.
When a metric suddenly drops or user behavior changes unexpectedly, you'll join the investigation. Can you break down a vague problem into specific hypotheses? Do you know what data to check and what patterns to look for? Can you separate real causes from coincidences?
You'll work through scenarios Uber actually faces: sudden drops in ride requests, unexpected driver behavior, or strange marketplace patterns.
Strong answers show a systematic approach, i.e., forming hypotheses, finding relevant data, checking for other explanations, and building toward a solid conclusion.
Example analytical execution questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Perform root-cause analysis on an operational issue.
- How would you investigate whether a particular trend in your data is an anomaly?
- How do you detect anomalies in a distribution?
- What trends indicate a healthy marketplace?
- What does price tell you in Uber's marketplace?
- How do you define a market?
- How would you anticipate the impact of a large event (such as a big concert or parade) on ride demand?
3.3 Product questions ↑
The best data scientists at Uber combine analytical rigor with product judgment. This section covers product sense, metrics definition, and marketplace economics: the business side of the role.
3.3.1 Product sense
Product sense questions test whether you understand products from both user and business angles.
At Uber, this means thinking about both sides of the marketplace: Why do riders choose Uber over competitors? Why do drivers accept some trips but not others? How do product changes affect the balance between supply and demand?
These questions are intentionally vague because real product problems are messy. There's rarely one right answer, but there are smart ways to think through the problem. Strong candidates identify the right user problems, consider competing objectives, and think through ripple effects.
For example, if Uber cuts rider prices, demand might increase. But if driver pay doesn't adjust, supply might drop, making the experience worse. Product sense means thinking through these connections rather than optimizing one metric in isolation.
Example product sense questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Describe how you would improve the Uber app.
- Pick your favorite product or app. How would you improve or redesign it?
- Why might a driver accept a ride that isn't financially optimal?
- If we added one rider to the San Francisco market, what happens to riders and drivers?
- How would you define driver incentives so they go to high-demand areas?
- Why does Uber's surge pricing exist, and how would you optimize it?
Check out our guides to product sense questions and the Meta product sense interview. These guides are geared mainly towards product managers, but their concepts are also applicable here.
3.3.2 Product metrics
Choosing the right metrics is fundamental to data-driven decisions, but at Uber, it's tricky because of marketplace dynamics. A metric that looks good for riders might be bad for drivers. Should Uber optimize for total trips, revenue per trip, or user satisfaction? How do you measure marketplace health when supply and demand depend on each other?
These questions test whether you can identify metrics that actually matter, not just metrics that are easy to count. Strong candidates distinguish between vanity metrics (impressive but useless), guardrail metrics (things to watch for problems), and decision metrics (measurements that actually inform choices).
You'll also need to show you understand trade-offs: faster matching might mean longer trips, surge pricing might boost revenue but hurt customer satisfaction. The goal isn't perfect metrics, but rather to thoughtfully balance competing goals.
Example product metrics questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- How would you measure the performance of a specific Uber business or feature?
- What metrics matter for the rider-driver matching algorithm?
- How would you evaluate Uber's estimated time of arrival algorithm?
- What are the performance metrics across different Uber services?
- What metrics would you use to track whether Uber's paid advertising acquisition strategy is working?
- What metrics would you track to evaluate paid advertising and determine acceptable customer acquisition cost?
- How would you measure Uber's impact on congestion or driving conditions?
- How do network effects influence experimental design and outcome measurement?
Learn more about acing product metrics interviews with this product metrics interview guide.
3.3.3 Marketplace economics
Uber's marketplace connects two groups (riders and drivers), creating unique economic challenges. Unlike a traditional business with one customer type, Uber must balance the needs of both sides simultaneously.
With two sides to satisfy, the company must carefully manage supply and demand in real time across hundreds of cities. Too many drivers can lower earnings and drive them away, while too few lead to longer waits and lost riders. These questions test your understanding of marketplace dynamics, pricing strategies, and incentives.
Strong candidates show they understand these problems are economic problems that require a balance between competing interests. You'll need to think about elasticity, network effects, and how changes on one side ripple through the entire marketplace.
Example marketplace questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Describe dynamic surge pricing and metrics that define supply and demand balance.
- If you were designing Uber Ride Pass for the first time, how would you set pricing?
- How would you price rides from scratch?
- How would you decide how many coupons to give Uber Eats customers?
- How would you predict ride requests?
- What affects ride request volume?
- How would you model driver acquisition?
- How would you best match a ride request to a driver?
3.4 Machine learning questions ↑
Machine learning questions focus on practical application rather than theory. While applied scientists and ML engineers build complex models for fraud detection and ETA prediction, data scientists need to understand when and how to apply ML to business problems.
These questions test whether you know which algorithms fit different situations, how to evaluate models, and how to explain model behavior to non-technical people. You might discuss building a churn prediction model, designing features for trip duration estimates, or handling imbalanced data in fraud detection.
Example machine learning questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- What is Random Forest? What's the intuition behind it?
- Explain LSTM and where you would use it.
- What is the cost function of Logistic Regression?
- What problems have you encountered with supervised ML, and how did you overcome them?
- How would you handle an imbalanced dataset?
- Do you have past experience working on ML projects? Walk me through one.
Read our guide to machine learning interviews for more guidance on these types of questions.
3.5 Statistics questions ↑
Statistical foundations are essential for Uber data scientists. Every experiment you design, every analysis you run, every conclusion you draw depends on statistics. These questions test both understanding and communication. You need to know what a p-value means and how to explain it to a product manager.
Uber's data scientists face challenges like multiple testing (running hundreds of experiments increases false positives), selection bias (active drivers aren't representative of all drivers), and confounding variables (seasonal patterns might hide or exaggerate real effects).
Strong candidates show statistical intuition: they know when assumptions break down and how that affects conclusions, they can spot biases, and they understand the difference between statistical significance and practical importance.
Example statistics questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Explain p-value to a non-technical person.
- What is the difference between MLE and MAP estimation?
- Explain the Central Limit Theorem.
- What are the assumptions of linear regression?
- How would you explain linear regression to:
- A child
- A first-year college student
- A seasoned mathematician
- Type I versus Type II errors: what are they, and which is worse?
3.6 Experimentation & causal inference questions ↑
Uber operates in a highly data-driven, fast-moving environment. Decisions impact millions of users and billions in revenue, so knowing what works and why is critical. Experimentation is how Uber validates those product changes before rolling them out.
You’ll find questions that assess your ability to design some of these rigorous experiments and extract causal insights from data, even when perfect randomization isn't possible.
3.6.1 A/B testing
A/B testing is fundamental to evidence-based product development at Uber. Every feature, pricing change, or algorithm improvement gets validated through experiments before full launch.
These questions test whether you can design experiments that produce reliable, actionable results. This means more than randomly splitting users. You’ll need to define success metrics, calculate the required sample size, set the experiment duration, and plan your analysis before collecting data.
Interviewers look for critical thinking about potential problems: What if users in different groups interact? How do you account for day-of-week patterns? What if your main metric doesn't change, but other metrics do?
Strong candidates show they understand that experiment design requires balancing statistical rigor with practical constraints, and interpretation requires judgment beyond just checking p-values.
Example A/B testing questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- How would you design an A/B test for a new feature?
- What are the assumptions of A/B testing?
- How do you explain statistical power to a product manager?
- How do you determine the sample size for an experiment?
- How do you run and interpret an A/B test?
3.6.2 Causal inference/experiment design
Causal inference goes beyond standard A/B testing to situations where randomized experiments are hard, impossible, or already contaminated. At Uber, you'll encounter scenarios where you need to estimate causal effects without perfect experimental control:
What was the real impact of a city-wide policy when you can't randomly assign cities? How do you measure surge pricing effects when it activates precisely when demand is high?
These questions test your understanding of techniques like difference-in-differences, regression discontinuity, and synthetic controls. More importantly, they test your judgment about when observational studies can credibly estimate causal effects versus when they'll mislead you.
Strong candidates understand the core problem (you can never see what would have happened without the treatment) and can explain what assumptions are needed to make causal claims from observational data.
Example causal inference questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Walk through a causal inference problem from your experience.
- How do you design an experiment to test a new policy?
- How do network effects influence your choice of experimental and control units?
- How do you estimate the impact of a feature rollout on key metrics?
3.7 Research & applied analytics questions ↑
These questions present open-ended business problems without clear solution paths. They mirror the ambiguous projects Uber data scientists actually work on: investigating why a metric changed, quantifying policy impact, or designing fraud detection systems.
Unlike structured technical questions, these problems require you to define the problem, propose an approach, anticipate challenges, and explain how you'd communicate findings.
Interviewers evaluate your ability to think creatively about data problems, break complex questions into manageable pieces, and design analyses that actually answer the business question instead of just producing numbers.
Strong candidates consider multiple approaches and explain trade-offs. They also acknowledge data limitations, recognize when perfect analysis is impossible, and propose pragmatic solutions that provide enough insight to make decisions with incomplete information.
Note: While there's some overlap with analytical execution questions, the key difference is in approach. Analytical execution focuses on diagnosis (what happened and why?), while applied analytics focuses on solution design (how would you build or estimate this?).
Example applied analytics questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- How would you estimate the efficiency of the carpool service?
- How would you design UberPool routing?
- How would you detect fraud from the driver side?
- How would you figure out competitor tipping patterns?
- How would you investigate whether Uber causes city congestion?
Note: While there's some overlap with analytical execution questions, the key difference is in approach. Analytical execution focuses on diagnosis (what happened and why?), while applied analytics focuses on solution design (how would you build or estimate this?).
3.8 Data quality/data governance questions ↑
Data quality is invisible until it's wrong, but at Uber's scale, quality issues can lead to terrible decisions. When you're analyzing billions of trips, even small error rates produce misleading conclusions.
These questions test whether you think critically about data before trusting it. Do you validate assumptions about completeness? Do you check for anomalies suggesting instrumentation problems? Can you tell when patterns reflect real changes versus data collection issues?
Strong candidates show healthy skepticism. They know what questions to ask about where data comes from, understand common failure modes in data pipelines, and can design checks to catch problems early. At Uber, where real-time decisions depend on accurate data, catching data quality issues before they affect products is invaluable.
Example data quality questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Have you ever worked on data visualization or data quality problems?
- How do you ensure dataset integrity before analysis?
- What kind of anomalies would make you distrust a dataset?
3.9 Time series & forecasting questions ↑
Forecasting is critical for Uber's operational planning. The questions test whether you understand time series patterns (trends, seasonality, holidays, special events) and can build models accounting for them.
Uber's forecasting is complicated by multiple interacting factors: weather affects demand, but surge pricing affects both demand and supply, and driver behavior changes based on expected earnings.
Strong candidates understand both forecasting techniques (ARIMA, exponential smoothing, Prophet) and practical considerations (How far ahead can you reliably forecast? How do you update forecasts as new data arrives?).
The goal here is to understand uncertainty and make decisions that work even when forecasts are wrong.
Example forecasting questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- What time series forecasting techniques are you familiar with?
- How would you forecast ride demand or vehicle availability?
- How are 2 time series different from one another? (Google)
3.10 Behavioral questions ↑
A significant portion of the Uber data scientist interview is made up of behavioral questions. These are meant to reveal how you’ve worked with others, responded to challenges, and made decisions in past roles.
Because data scientists at Uber operate in fast-paced, cross-functional environments, interviewers are looking for evidence that you can communicate clearly, navigate ambiguity, and take ownership of your work.
Come prepared with a list of stories from your past experience that you can use to answer questions such as the ones below.
Example behavioral questions asked at Uber data science interviews:
- Tell me about yourself.
- Why are you applying to Uber? (See sample answers for Amazon.)
- What do you want from your next job?
- What makes you a strong candidate for this role?
- How many years of experience do you have?
- Tell me about a time you collaborated cross-functionally.
- What kind of problems have you faced in previous roles?
- What did you like or dislike about your previous jobs?
- Tell me about a project you've worked on.
For more practice, we also recommend using our list of 16 most-asked behavioral interview questions, which includes tips and sample answers.
Also, if you need even more questions to practice with, you can also take a look at our data science interview prep guide.
4. Uber data scientist interview tips ↑
You might be an excellent data scientist, but unfortunately, that's not necessarily enough to ace your interviews at Uber. Interviewing is a skill in itself that you need to learn.
Let's look at some key tips to make sure you approach your interviews in the right way.
4.1 Understand Uber's two-sided marketplace dynamics
Uber's core business is a two-sided marketplace connecting riders and drivers. This creates unique challenges around network effects, supply-demand balancing, and interdependent metrics. When answering questions, demonstrate your understanding of how changes to one side of the marketplace affect the other.
For instance, if asked about driver incentives, consider the downstream effects on rider wait times, pricing, and overall platform liquidity. Interviewers are looking for candidates who can think holistically about marketplace dynamics.
4.2 Be data-driven in your approach
Uber is a highly data-driven company, as noted by sources on Blind. When answering questions, ground your responses in data and metrics. Even if you don't have access to actual data during the interview, explain what data you would collect, how you would measure success, and what metrics you would track.
When discussing past projects, come prepared with specific KPIs, percentage improvements, and quantifiable impact. Numbers matter at Uber.
4.3 Master SQL window functions
SQL questions at Uber heavily emphasize window functions like PARTITION BY, LAG, LEAD, ROW_NUMBER, and RANK. Make sure you're comfortable writing complex queries with these functions, as they appear frequently in both the technical screen and onsite rounds.
Practice solving medium-difficulty SQL problems on platforms like DataLemur, StrataScratch, or the LeetCode SQL section. Focus on problems involving window functions, date manipulations, and multi-table joins.
4.4 Communicate your thought process clearly
During coding and case study interviews, think out loud. Interviewers care as much about your problem-solving approach as your final answer, according to Uber EM Tatiana Maluf. Walk them through your reasoning, explain trade-offs, and articulate why you're making specific choices.
For SQL queries, explain your logic before writing code. For product cases, structure your thinking using a framework. For A/B tests, outline your experimental design step by step. Clear communication demonstrates structured thinking and makes it easier for interviewers to follow your logic.
4.5 Understand the limitations of A/B testing at Uber
Network effects make traditional A/B testing challenging at Uber. If a driver in the treatment group receives higher pay, nearby control group drivers might experience lower ride requests, contaminating your experiment. Be prepared to discuss alternatives like switchback tests, geo-based experiments, or difference-in-differences approaches.
When asked about A/B testing, acknowledge these challenges and explain how you would design experiments that account for marketplace interdependencies.
4.6 Frame everything in terms of business impact
Data science at Uber is about driving business outcomes, not just building models. When discussing projects or answering case questions, always connect your work to business impact. How did your analysis increase revenue? How did your model improve user experience? How did your experiment inform product decisions?
Interviewers want to see that you understand the "why" behind the data work, not just the "how."
4.7 Prepare for scenario-based questions
Many questions at Uber are framed as real business scenarios. You might be given actual data from Uber's operations and asked to extract insights or make recommendations. These questions test your ability to apply technical skills to ambiguous, real-world problems.
Practice with case studies that involve marketplace dynamics, pricing optimization, demand forecasting, and fraud detection. The more you practice thinking through messy, open-ended problems, the more comfortable you'll be in the interview.
4.8 Demonstrate humility and collaboration
Uber values candidates who can work effectively with cross-functional teams. When answering behavioral questions, emphasize the times you collaborated with product managers, engineers, or other stakeholders. Show that you can incorporate feedback, handle disagreement constructively, and prioritize team goals over individual ego.
Data science at Uber is a team sport. Interviewers want to see that you'll be a positive, collaborative addition to their team.
4.9 Study Uber's products and challenges
Before your interviews, familiarize yourself with Uber's products beyond just ride-sharing. Understand Uber Eats, Uber Freight, and how the platform operates. Read Uber's engineering blog posts, challenges with surge pricing, driver retention issues, and the competitive landscape.
When you can reference specific Uber products or challenges in your answers, it demonstrates genuine interest and helps interviewers envision you in the role.
4.10 Practice coding without IDE support
Uber's technical screens are conducted on platforms like CoderPad or CodeSignal, which have limited functionality compared to full IDEs. You won't have autocomplete, syntax highlighting, or easy debugging tools.
Practice writing SQL and Python code in simple text editors to get comfortable with this constraint. Focus on writing clean, readable code that you can debug by inspection.
5. Preparation plan ↑
Now that you know what to aim for in your interviews, let's focus on preparation.
We've coached more than 20,000 people for interviews since 2018. There are essentially four activities you can do to practice for interviews. Here's what we've learned about each of them.
5.1 Learn more about the company
Most candidates fail to do this. But before investing tens of hours preparing for an interview at Uber, you should take some time to make sure it's actually the right company for you.
Uber is prestigious, and it's therefore tempting to assume that you should apply without considering things more carefully. However, it's important to remember that prestige alone won't make you happy in your day-to-day work. What will make you happy is what you'll actually be doing as well as the people you'll be working with.
If you know data scientists who work at Uber (or used to), talk to them to understand what the culture is like. In addition, we recommend reading the following resources:
- Uber's values
- Uber interview process overview
- Uber's strategy teardown (by CB Insights)
- Uber Engineering Blog
- Uber Data/ML Blog
- Candidate reviews on Glassdoor and Blind
5.2 Practice by yourself
Learning by yourself is an essential first step. We recommend you make full use of the free prep resources on this blog (including our main data science interview prep guide). That way, you can see what an excellent answer looks like.
For SQL practice, use platforms like:
Focus on medium-difficulty problems involving window functions, joins, and date manipulations.
For statistics and A/B testing, review fundamental concepts like hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, statistical power, and experimental design. Practice explaining these concepts in simple terms, as you'll need to communicate technical ideas to non-technical stakeholders.
For product sense questions, practice using the BUS framework (Business Objective, User Problems, Solutions), which applies well to data science product interviews.
Once you're in command of the subject matter, you'll want to practice answering questions. But by yourself, you can't simulate thinking on your feet or the pressure of performing in front of a stranger. Plus, there are no unexpected follow-up questions and no feedback.
That's why many candidates try to practice with friends or peers.
5.3 Practice with peers
If you have friends or peers who can do mock interviews with you, that's an option worth trying. It's free, but be warned, you may come up against the following problems:
- It's hard to know if the feedback you get is accurate.
- They're unlikely to have insider knowledge of interviews at your target company.
- On peer platforms, people often waste your time by not showing up.
For those reasons, many candidates skip peer mock interviews and go straight to mock interviews with an expert.
5.4 Practice with experienced data science interviewers
In our experience, practicing real interviews with experts who can give you company-specific feedback makes a huge difference.
Find an Uber data scientist interview coach, so you can:
- Test yourself under real interview conditions
- Get accurate feedback from a real expert
- Build your confidence
- Get company-specific insights
- Learn how to structure your answers better
- Save time by focusing your preparation
Landing a job at a big tech company often results in a $50,000 per year or more increase in total compensation. In our experience, three or four coaching sessions worth approximately $500 make a significant difference in your ability to land the job. That's an ROI of 100x!
Click here to book Uber data scientist mock interviews with experienced interviewers.