Today we're going to cover the top case interview frameworks, as well as how you can create your own custom frameworks.
Understanding frameworks has always been critical for the 8,000+ candidates who we've helped with consulting interview preparation.
And one of the first things you'll want to know is that you should AVOID using pre-made frameworks, like those recommended in Case in Point and in Victor Cheng's LOMS programme. But more on that later.
Let's start with the list of top frameworks.
- Top 7 frameworks for case interviews
- 1. Profitability
- 2. 4Ps
- 3. Porter's 5-forces
- 4. 3Cs
- 5. Market entry
- 6. Pricing
- 7. Merger and acquisition
- Don't reuse pre-existing frameworks
- How to create custom frameworks
Click here to practise 1-on-1 with MBB ex-interviewers
Top 7 frameworks for case interviews
1. Profitability framework
The profitability framework is the most basic framework in business analysis. It simply breaks down profit into its basic revenue and cost components and is commonly used to identify the root cause of profitability issues.

- Revenue can simply be broken down into the Number of Units Sold x Price Per Unit.
- Costs can be broken down into Variable and Fixed Costs. And Variable Costs can be further broken down into the Number of Units Produced x Cost Per Unit.
2. The 4Ps framework
The 4Ps framework is widely used by company executives to design their marketing strategy. There are different variations of this framework, which is also sometimes referred to as the “Marketing mix” framework, but the 4Ps is the most common one.
This framework is commonly used when launching a new product or when reviewing the positioning of an existing product.

- Product: What are the key characteristics of the product sold? Key elements of the product definition could include: customer need fulfilled by product, product usage (E.g. who, where, how, etc.), good vs. service, product lifecycle (new vs. established), competing products and substitutes, etc.
- Price: At what price should the product be sold? Different considerations need to be taken into account here: the customer perceived value of the product, the price of competitive products, the customer price sensitivity, the cost of producing the product, etc.
- Promotion: Which promotion strategies should be used to sell the product? Key elements to consider include: promotion messages, media type (E.g. TV, social media, radio, etc.), best time to promote, competitors’ strategies, etc.
- Place: Through which channels should the product be distributed? Key elements to consider include: possible channels to distribute the product (E.g. in store, web, mail-to-order, etc.), customer expectations in terms of channel, requirement of a sales team or not, competitors’ strategies, etc.
3. Porter's 5 forces
Porter’s 5 forces is a framework commonly used by CEOs to explore the competitive dynamics of industries. Indeed not all industries are structured the same way.
Some industries are really hard to get into (E.g. banking) while others have very low barriers to entry (E.g. newspapers).
Suppliers have strong bargaining power in some industries (E.g. high-end medical equipment) but little power in others (E.g. small milk producer), etc.
Understanding these dynamics is extremely important when you're considering entering a new industry or when assessing the competitive dynamics of the industry a company is already in.

- Bargaining power of customers: How much bargaining power do customers have? If there is only one buyer but multiple suppliers, then that buyer will be at a strong advantage. Key elements to consider here include: customer concentration (percentage of industry revenues from Top 3 buyers), customer price sensitivity, customer information availability, etc.
- Bargaining power of suppliers: How much bargaining power do suppliers have? Similarly to the previous point, if there is only one supplier but multiple buyers, then that supplier will be at a strong advantage. Key elements to consider include: concentration of suppliers (percentage of industry revenues to Top 3 suppliers), difficulty of switching from one supplier to another, differentiation between suppliers, etc.
- Threat of substitutes: What are the substitutes for the product and are they increasingly popular? As a reminder, water is a substitute for Coke while Pepsi is a competitive product for Coke. Key elements to consider here include: potential new substitutes, ease of substitution, evolution of customer propensity to substitute, etc.
- Threat of new entrants: How difficult is it to enter the industry for potential new players? Key elements to consider here include: regulation authorisations, capital requirements, economies of scale, network effects, etc.
- Existing rivals: How competitive are existing rivals in the industry? Key elements to consider include: number of competitors and their market shares, similarity between their products and products of the firm analysed, financial health of competitors, etc.
4. 3Cs framework
The 3Cs framework is also commonly used to put together strategies for companies. As you will notice below, a lot of its components overlap with the Porter’s 5 forces.
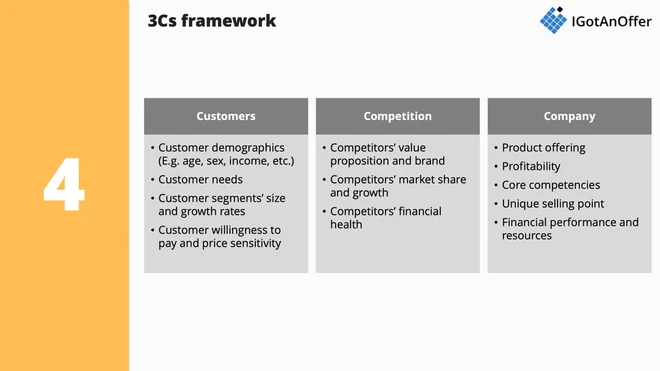
- Customers: Who is the customer? Key elements to consider include: customer demographics (E.g. age, sex, income, etc.), customer needs, customer segments' size and growth rates, customer willingness to pay and price sensitivity, etc.
- Competition: What are the competitive dynamics? Key elements to consider include: competitors’ value proposition and brand, competitors’ market share and growth, competitors’ financial health, etc.
- Company: What defines the company? Key elements to consider include: product offering, profitability, core competencies, unique selling point, financial performance and resources, etc.
5. Market entry framework
The market entry framework is commonly used to make decisions on whether a company should enter a new market or not.
For instance, you could use it to decide if Starbucks should enter the Chinese market, or if Nike should enter the sports broadcasting business.

- Market: What are the characteristics of the market we are trying to enter? Key elements to consider include: market size and profitability, products already available in the market, intensity of the competition, heaviness of the regulation, etc.
- Client capabilities: Does the client have the right capabilities to enter that new market? Key elements to consider include: differences between the client's current market and the new one they are now targeting, number of times client has entered new markets and achieved success, other companies already in the new market, etc.
- Financials: Does it make financial sense to enter the new market? Key elements to consider include: current financial situation of the client, cost to enter the new market, ongoing costs once the market is entered, expected revenues and return on investment, etc.
- Entry strategy: How should the client go about entering the new market? Key elements to consider include: timing of market entry (now vs. delay), speed of market entry (test region vs. whole country), opportunity to buy competitor or do a JV, management approach (control from HQ vs. decentralise), etc.
6. Pricing case framework
Companies always face a difficult issue when launching a new product or service. What should its price be? The pricing framework is extremely helpful for answering that question.

- Cost-based: What price do we need to set to cover all our costs? Key elements to consider include: fixed costs and their allocation across products, variable costs and number of units produced / sold, profitability targeted, etc.
- Value-based: How much are customers willing to pay for our product? Key elements to consider include: price of the next best alternative to our product, features that make our product better than the next best alternative, value of these features, etc.
- Competitor-based: What is the competition charging for similar products? Key elements to consider include: available substitute products from the competition, price of these substitute products, value of our product vs. substitutes, etc.
- Overall strategy: Given the elements above, what should our pricing strategy be? Key elements to consider include: objective of the pricing strategy (E.g. high profitability or high market share), opportunities for upsell / cross-sell that should be taken into account (E.g. Kindle and ebooks), possibility to sell different versions of the same product (E.g. iPhone 13 and iPhone 13 Pro), etc.
7. Merger and acquisition framework
Finally, the merger and acquisition framework is used when companies are looking to acquire or merge with competitors.
These situations are not very frequent in a CEO's life, but they are highly stressful, which is one reason why consultants are often asked to support such initiatives.
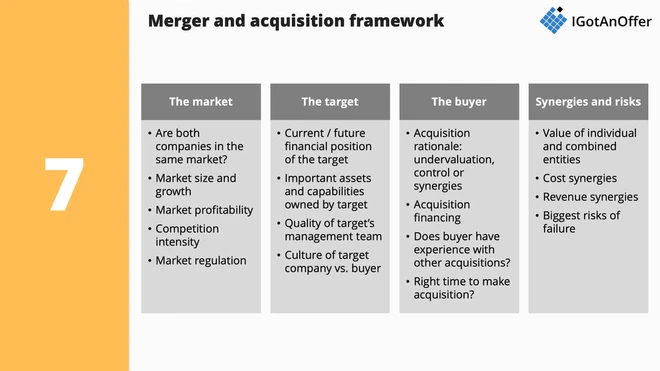
- The market: What are the characteristics of the target company's market? Key elements to consider include: market size and growth, market profitability and intensity of the competition, market regulation, etc.
- The target: How attractive is the target to be acquired? Key elements to consider include: current and future financial position of the target, important assets or capabilities owned by the target, quality of the target's management team, target / buyer culture fit, etc.
- The buyer: What's driving the buyer to make the acquisition? Key elements to consider include: acquisition rationale (E.g. target undervalued, etc.), acquisition financing, buyer's acquisition experience, acquisition timing, etc.
- Synergies and risks: What are the acquisition synergies and risks? Key elements to consider include: value of individual and combined entities, cost synergies, revenue synergies, biggest risks of failure, etc.
Don't reuse pre-existing frameworks
Once you are generally familiar with frameworks, the question becomes: how do you actually use frameworks in case interviews?
There are a lot of opinions about how you should do this on the Internet. But the two main schools of thought are Marc Cosentino’s Case In Point and Victor Cheng’s LOMS.
But both of these methods share the same flaw: they try to force pre-defined frameworks onto cases. In our experience, this is bound to produce average results because all cases are unique.
Not convinced? Let's cover each of these two popular methods in more detail.
Why NOT to use the Case In Point frameworks
In Case In Point, Marc Cosentino attempts to classify case interviews into 10+ categories and then suggests that candidates should memorise a specific framework for each of them.
This is an interesting exercise as it exposes you to a range of business problems and helps you think about them in different ways. However, in our experience, learning 10+ frameworks is difficult and time consuming.
More importantly, in live case interviews, trying to recognise one of the 10+ case categories and then remembering the associated framework is a real nightmare!
Instead of focusing on solving the problem at hand, you end up trying to remember a framework that will not even perfectly fit the case you are solving. In our experience, the best candidates avoid this strategy.
Why NOT to use Victor Cheng's LOMS frameworks
In his LOMS programme, Victor Cheng advocates for a much simpler method and suggests you should only learn two frameworks: the profit framework for profitability cases, and a general framework for all other cases (Product, Consumer, Company, Competition).
The benefit of this approach is its simplicity. It gives you a starting point that’s easy to remember when you are putting a framework together.
However, in our experience, this approach has a fatal drawback. In practice, there aren’t that many profitability cases, and you basically always end up using the general framework.
Even if you adapt this general framework, it won't be perfectly tailored to the case you are trying to solve. More importantly, your interviewer will quickly realise that you are using a pre-made framework and that will reflect negatively on you.
Why to create custom frameworks instead
A good framework is a bit like a tailor-made suit: it is adapted to the problem you are trying to solve, the company, the industry, and it is also as MECE as possible.
If you use pre-existing frameworks, you run the risk of missing important elements of the specific problem you are trying to solve. In real life, consultants rarely use pre-defined frameworks. They are familiar with them, but they do not directly re-use them as-is on projects.
Instead, they create a customised framework or issue tree that addresses the specific details of each case. To do so, they rely on conversations with their client as well as past experiences.
This might sound intimidating, but the good news is that creating custom frameworks is actually much simpler than you might think.
How to create custom frameworks
Now, let's turn our attention to HOW you can create your own custom frameworks during case interviews.
Here's a brief summary of the steps you'll need to take:
Summary - IGotAnOffer method (framework development questions)
- Step 1: Ask for time to gather your thoughts
- Step 2: Create the framework
- Extract the main elements from the case question
- Break down the main elements into components
- Step 3: Communicate the framework
- Spin your paper around
- Begin with an overview
- Highlight 3-5 considerations for each branch
- Summarise your points
- Prioritise next steps
Now let's cover these steps in more detail. We'll also be digging into a real case example below, in order to illustrate the framework creation process.
1. Ask for time to gather your thoughts
Regardless of the case you get, you should always ask your interviewer for some time to gather your thoughts, before you begin to develop the framework.
This is a normal part of the interview process. Your interviewers will expect you to ask, and they'll almost always give you this time.
But don't get carried away!
For reference, you should only take 30-60 seconds to quietly think-through your framework. We recommend that you also sketch out your framework on a piece of paper during this time, as that will help you to organise your thoughts more clearly.
Without practise, it's really difficult to estimate how long 30-60 seconds actually is, so we highly recommend that you practice this process with a stopwatch. This exercise will help you get a clear idea of how much time you're actually using.
2. Create the framework
During that 30-60 second time window, you'll need to do the real work of crafting your framework.
The essence of framework creation is actually quite simple. A framework takes the business situation presented in the case, and breaks it into smaller "bite size" pieces.
By isolating the various components of a case, you'll be able to better identify the root cause of an issue, or find the best opportunities for improving the underlying business.
And the best way to develop your framework creation skills is with practice on realistic case problems, so let's walk through an example together.
Star Production case example
Star Production is a start-up that produces low-cost movies. Two university friends created the company after watching “Paranormal Activity”, a low-budget movie that attracted a larger-than-expected audience.Very few low-cost movies end up being very successful. Star Production is hoping to generate profits by producing a large number of low-budget movies and betting that some of them become very successful. The company forecasts that most of its movies will be loss making but that a few of them will be big financial hits.
Considering the high up-front cost of production, and the low probability of success of low-budget movies, the two friends are evaluating the best ways to finance the company. They have hired you to help them develop a business plan that can convince investors that their model is sustainable.
What areas would you look at to determine if Star Production’s business model can be sufficiently profitable to recoup initial investments in the short term?
In this case we need to analyse the short-term profitability of a movie production company. So, you would begin crafting your framework by thinking about the different factors that would contribute to the company's overall profits.
The first two components of this framework are fairly straightforward: revenues and costs. That's because the profitability of any company is determined by a combination of their revenues and costs.
Then, we can further deconstruct both revenues and costs based on our knowledge (or perhaps some assumptions) of the movie production business. And as you break down the components further, it's important to consider the concept of MECE, which stands for Mutually Exclusive Collectively Exhaustive.

In simple terms, MECE means that you should aim to have a framework where the branches do NOT overlap with each other, and where the framework is comprehensive (i.e. no branches are missing). You can learn more about this in our separate MECE guide.
Now here's an example of what your draft framework might look like for the Star Production case:

As you can see in the example above, we've broken down the revenues and costs into specific components that would make sense for a movie production business.
And we've used bullet points to highlight the information we would need in order to determine how each individual item contributes to the overall revenues or costs of the business.
For example, we would need to know the expected ticket sales, the average ticket price, and the share of the ticket revenue that Star Production would be entitled to, in order to calculate the total ticket revenue.
Once you've drawn out a rough framework like the above example, your next task will be to explain your framework to your interviewer.
3. Communicate the framework
Even if you created the world's best framework, it won't get you an offer if you're not able to explain it in a clear and structured way.
Here's how we'd recommend you communicate your framework during your interviews:
Spin your paper around
Start by showing your interviewer the framework that you've drawn on paper. Having this visual structure will make it much easier to explain (and understand).
Start with an overview
Before jumping into the details of your framework, you should start with an overview of the framework.
In our example above, you could simply explain that the profitability of Star Production will be determined by the expected revenues and costs of the business, which can be broken down into more specific categories.
You should also tell your interviewer the order in which you plan to walk through each individual branch, so they'll know what to expect.
Highlight 3-5 considerations for each branch
Next, go through each branch of your framework and mention several considerations that came to mind while you were drafting the framework.
For example, for the "upfront costs" branch of the Star Production case, you could explain that you'd want to find out what costs the company would incur before it can start releasing movies, like filming equipment, studio space, and post production expenses.
Summarise your points
And throughout your explanation of the framework, you should pause periodically to summarise your key points, and to check in with your interviewer.
You're likely going to be covering a lot of ground in your framework, and you want to make sure that your logic doesn't get foggy in the details.
For example, you could summarise the most important considerations that impact the revenues of Star Production, after you've walked through each individual sub-branch under revenues.
Prioritise next steps
Finally, after walking through your full framework, you should tell your interviewer the 2-3 next steps you would recommend, in priority order.
There's a variety of ways you could rank next steps, but three good options would be based on importance, ease, or speed.
Returning to the Star Production example, you could recommend the following next steps in priority order:
- Identify the biggest cost drivers. Star Production's business model is focused on producing a high volume of low cost movies, so controlling costs will be essential to the profitability of the company.
- Develop a production process that minimises costs. Once the primary cost drivers are identified, we should develop a production process that keeps those costs as low as possible.
- Look for opportunities to increase the hit rate. Star Production is counting on a few box office hits to drive revenues. As a result, increasing the percentage of movies that succeed could be a big win.
Get MBB offers by mastering frameworks
To succeed in case interviews, you MUST be able to create and apply frameworks effectively. And if you really want the best possible preparation for your case interview, you'll want to practise doing this in an interview situation, ideally with an expert consultant giving you feedback.
The IGotAnOffer team
Photo: Roberto Taddeo / IM